National Grants
Project's code: PN-III-P4-ID-PCCF-2016-0172
Project's title:Targeting innate immune mechanisms to improve risk stratification and to identify future therapeutic options in myocardial infarction
Contract number: 05/18.07.2018
Coordinator: Acad.Maya Simionescu
Research Partners:
CO: Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology "Nicolae Simionescu"
P1: University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology, TARGU MURES
P2: University of Medicine and Pharmacy "CAROL DAVILA" BUCHAREST
Budget: 8.500.000 Lei
Period: 18.07.2018 – 31.06.2022
Project's team:
|
CO: Maya Simionescu - Project coordinator Manea Adrian Elena Butoi Felicia Antohe Mihai Bogdan Preda Madalina Ioana Fenyo Monica Madalina Tucureanu Elena Uyy Andrei Vacaru Viorel Suica Raluca Boteanu Simona-Adriana Manea Luminita Ivan Sinziana Popescu Razvan Daniel Macarie Mihaela Loredana Antonescu Alexandra-Gela Lazar Mihaela Vadana Letitia Ciortan Sergiu Cecoltan Angelica-Ramona Tuchilus |
P1: Alexandru Schiopu – P1 coordinator Ovidiu Cotoi Eliza Russu Razvan Mares Bogdan Cordos Goran Marinkovic Peter Olah
|
P2: Dragos Vinereanu – P2 coordinator Lucia-Stefania Magda Sorina Mihaila Baldea Ruxandra Dragoi Antunes Guerra Galrinho Janina Diana Mihalcea Roxana Cristina Rimbas Livia Trasca
|
Abstract:
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. At present, clinicians lack specific biomarkers for accurate post-MI risk stratification and therapeutic tools to modulate myocardial inflammation and to promote efficient recovery. Innate immune processes mediated by polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) and macrophages (MAC) in the immediate post-MI period determine the extent of myocardial damage but also induce repair. Our major goal is to identify central molecules that mediate the crosstalk between sub-populations of PMN and MAC, and determine their involvement in MI. Additionally, we will test the ability of specific therapies to regulate myocardial inflammation and to improve cardiac function in-vivo. Project objectives are: (1) To identify key mediators that determine post-MI myocardial remodeling and prognosis – We will investigate the relationships between the soluble PMN/MAC mediators, post-MI cardiac function and prognosis in MI patients; (2) Investigation of the crosstalk between PMN and MAC in MI – We will use in-vitro studies, genomics and proteomics to identify mediators that govern the PMN-induced MAC polarization into sub-populations that promote repair. The role of the identified molecules will be tested in-vivo; (3) Development of a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-based therapy in MI – We will investigate the ability of MSC treatment to shift PMN and MAC polarization towards reparatory phenotypes, and to improve cardiac recovery; (4) To investigate S100A8/A9 blockade as potential therapy in MI – S100A8/A9 is a potent pro-inflammatory molecule secreted by PMN and MAC. We will assess whether S100A8/A9 blockade inhibits inflammation and improves post-MI cardiac function. The expected outcome is to identify biomarkers that can be used to accurately identify patients at high risk to suffer new events. MSC therapy or S100A8/A9 blockade might improve recovery of MI patients and reduce morbidity and mortality in this large patient group.
Project’s objectives:
Objective 1. Identify immune mediators involved in the dynamic crosstalk between PMN and Mac sub-populations that modulate the inflammation/repair balance post-MI (CO, P1, P2).
Objective 2. Assess blockade of the PMN mediator S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) as a potential therapy to inhibit inflammation and promote cardiac repair post-MI.(P1 and CO).
Objective 3. Exploiting the immuno-modulatory properties of MSC to reduce inflammation and promote myocardial recovery post-MI (cell therapy) (CO, P2).
Objective 4. Validate the clinical relevance of key innate immune mediators identified in Objectives 1-3 as potential biomarkers reflecting cardiac remodelling, prognosis, and response to treatment in patients with MI (CO, P1, P2).
RESULTS
In the 2018-2020 period, within the Objective 1 “Identify immune mediators involved in the dynamic crosstalk between PMN and MAC sub-populations that modulate the inflammation/repair balance post-MI” (Fig 1), weinvestigated: (1) N1 and N2 neutrophil phenotypes and functionality (in vitro); (2) Characterization of macrophage phenotypes after exposure to PMN secretome; (3) Identification of the soluble mediators present in the N1- and N2- PMN secretome that regulate MAC polarization and (4) the ability of PMN mediators to induce macrophage efferocytosis.
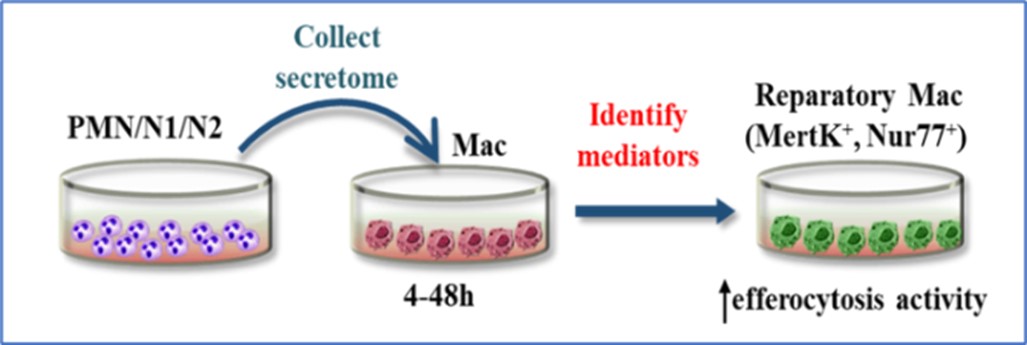
Figure 1. Representation of the experimental procedure of objective 1
The results obtained until now revealed that secretome derived from N1 and N2 PMN triggered the expression of specific markers of M1 or M2 MAC, namely N1-derived secretome induced M1 polarization whereas N2-derived secretome induced the expression of M2-MAC specific markers in vitro. Moreover, the efferocytosis experiments revealed that M2a and M2c macrophages are more efficient in clearing apoptotic HCM cells than M1 subset.
In the myocardial injury another important molecule is the alarmin S100A8/A9 that is one of the first signals that triggers an innate immune response. It is released from necrotic cardiomyocytes and activated PMN, and increases rapidly in the myocardium and in the systemic circulation after an MI. The S100A8/A9 binds to specific receptors TLR4 and RAGE, and leads to secretion of inflammatory cytokines that are instrumental in the initial inflammatory phase post-MI. These actions lead to the recruitment of phagocytes into the infarcted myocardium and highlight the importance of this alarmin for disease evolution. Therefore, as a therapeutic strategy for MI, we hypothesized that adequately timed S100A8/A9 blockade might inhibit local and systemic inflammation, reduce myocardial damage, and might be used as a novel therapy to promote cardiac repair post-MI. This hypothesis is achieved in the Objective 2. Assess blockade of the PMN mediator S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) as a potential therapy to inhibit inflammation and promote cardiac repair post-MI”. In the 2018-2020 period, we investigated (1) the Impact of S100A8/A9 blockade on cardiac function and post-MI remodelling, (2) histological assessment of the effects of ABR-238901 treatment (an inhibitor of S100A8/A9) on immune cell infiltration, apoptotic cell clearance, fibrosis and neovascularization, and (3) examined the impact of ABR-238901 on the local and systemic immune cell environment, using a mouse model of MI. The experimental design is shown in Fig 2.

Figure 2. Short-term in-vivo S100A8/A9 blockade experiment layout
The main results obtained until now highlighted that post-MI, long-term S100A8/A9 blockade with the specific molecule ABR-238901 worsen the cardiac function, increased cardiac remodelling and induced larger myocardial damage. Conversely, short-term S100A9 blockade with ABR-238901 reduces myocardial inflammation and improves cardiac function after an MI (Fig 3). We believe that the underlying mechanisms of these effects are related to diminished number of neutrophils and monocytes as well as of S100A8/A9 levels in the myocardium, tipping the M1/M2 balance towards a reparatory response. Ultimately, these effects lead to a significant improvement of cardiac function in murine models of MI induced by permanent coronary artery ligation and ischemia/reperfusion. Our studies identify for the first time the importance of S100A9 in MI, and promote ABR-2328901 as a potential clinically relevant treatment aiming to reduce cardiac damage and to improve prognosis in MI patients.
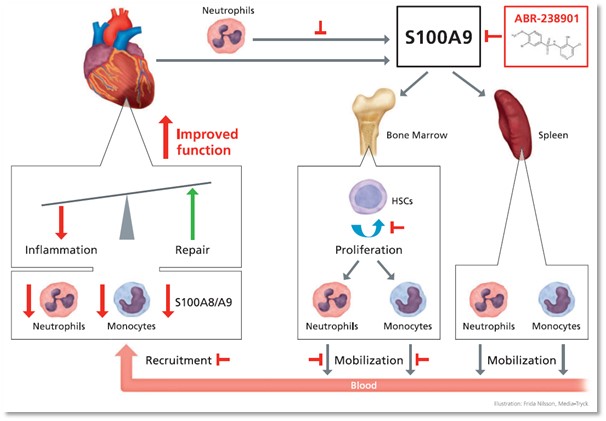
Figure 3. Schematic representation of the local and systemic effects of S100A9 blockade with ABR-238901 post-MI. (Marinkovik et al., European Heart Journal 2019)
Another therapeutic strategy for MI and a challenge in biomedical research is the regeneration of damaged tissue. Owing to their therapeutic effects, mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have become an attractive option for boosting tissue repair after injury. The effector properties of MSC have been linked to their ability to protect from apoptosis and stimulate angiogenesis, to support stromal remodelling and to modulate the immune responses. Reports from our and other laboratories have showed that MSC secreted molecules have a local protective effect on the microenvironment. Moreover, several studies support the idea that some of the therapeutic effects of MSCs are mediated by endocrine-like mechanisms, suggesting that homing to the site of injury is not necessarily required for therapeutic efficacy, as long as it can be achieved from remote sites. Thus, we design experiments and employed a mouse model of MI to cover the objective 3 “To develop a cell therapy employing the immunomodulatory properties of MSC for cardiac repair post-MI. This part of the project is already in the calibration phase trying to identify the best strategy capable to obtain the maximum benefits”. In the2018-2020 period we assessed: (1) the optimal MSC-based treatment strategy: cell number, delivery route and dose transplantation and (2) the effect of MSC on the phenotype of PMN and MAC in the post-MI inflammatory process, in vivo.
The preliminary results suggest that subcutaneous transplantation of MSC is a better approach than the intravenous route, in terms of long-term survival of cells in vivo, after transplantation. Moreover, remote MSC-based therapy (in multiple doses) showed morphological and functional improvements of the infarcted hearts, in part by modulating the reparatory immune cell populations and promoting tissue repair after injury.
In the 2020-2021 period, within the Objective 1 “Identify immune mediators involved in the dynamic crosstalk between PMN and MAC sub-populations that modulate the inflammation/repair balance post-MI” (Fig 1), we have found that:
(1) the secretome derived from N1 or N2 neutrophils exhibits distinct proteomic profile as compared with control (C) (Fig 4 and fig. 5), while the functional enrichment bioinformatic analysis revealed the over-representation of potential key signalling pathways such as oxidative stress and redox pathway and integrin-mediated cell adhesion that were specific for the N1 phenotype and Neutrophil extracellular trap formation that was only specific for the N2-type secretome.
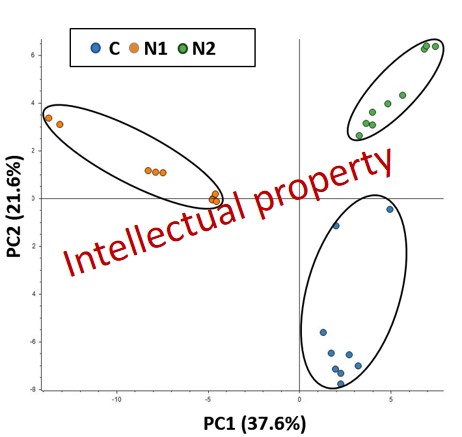
Figure 4: Principal Component Analysis of the control secretome (blue dots), N1-type phenotype secretome (orange dots) and N2-type phenotype secretome (green dots).
Therefore, from the 655 differentially abundant proteins, the normalization on control samples revealed 436 proteins that were significantly down-regulated and 156 that were up-regulated when comparing the N1-type phenotype secretome (Fig. 5a). Similarly, in the case of the anti-inflammatory N1-type secretome we obtained 279 down-regulated and 83 up-regulated proteins (Fig. 5b)
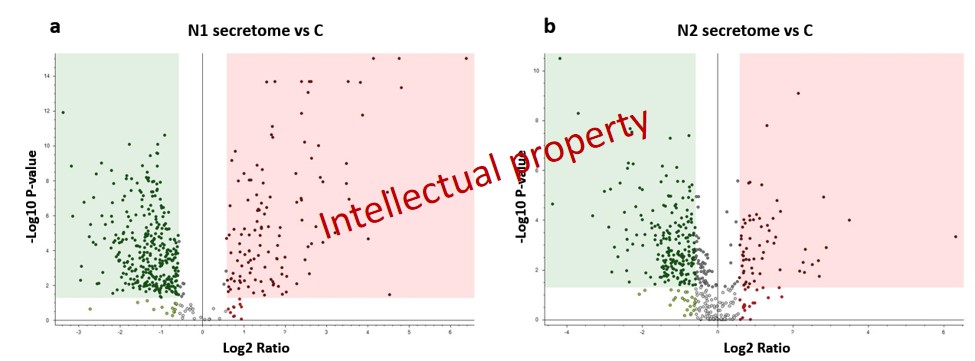
Figure 5: Volcano plots revealing the alteration tendencies of the N1-type secretome (a) and N2-type secretome(b) when comparing them to the control samples.
(2) Pharmacological inhibition of alarmin S100A9 by ABR-238901 reduces NADPH oxidase expression in the infarcted myocardium in mice. As shown in the figure 6, Nox2 subtype is localized in the Mac-rich area within ischemic myocardium.
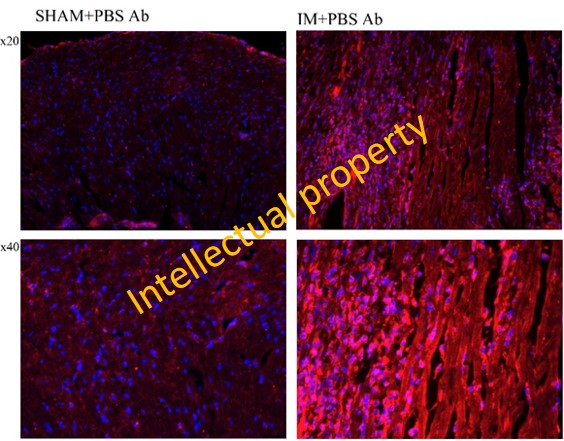
Figure 6. Immunolocalization of Nox2 by IF microscopy within the myocardium of sham-operated mice and MI mice. Nox2 - the prototypical NADPH oxidase subtype expressed by professional phagocytes (PMN, Mac).
Moreover, the data we have found suggest that pharmacological inhibition of S100A9 reduces the expression of genes defining the pro-inflammatory phenotype of macrophages in the ischemic myocardium of mice and in S100A9-challenged Mac, and S100A8/A9 could become a complementary therapeutic target to alleviate both inflammation and oxidative stress in MI.
(3) The gene expression analysis on human neutrophils revealed that N1 neutrophils have an inflammatory phenotype, with increased expression of most important inflammatory molecules including IL-1β, IL-6 or S100A9. Human neutrophils were isolated and stained using Giemsa protocol and the specific polymorphonuclear nucleus of neutrophils are shown in the figure 7.
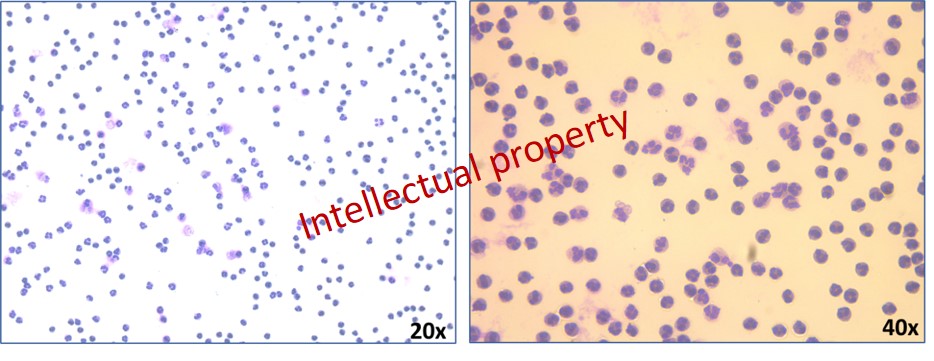
Figure 7. Neutrophil staining using Giemsa protocol (20x and 40x enlargement) clearly outline the polymorphonuclear nucleus of isolated neutrophils.
Moreover, the efferocytosis procees was investigated in macrophages exposed to N1 or N2 conditioned media. As known, efferocytosis occurs through a unique phagocytic mechanism reliant on the successful completion of three distinct steps: i) “find-me” signals such as lysophosphatidylcholine (LPS) are released from apoptotic bodies, inducing recruitment of phagocytes to the apoptotic cell; ii) phagocytes bind apoptotic corpses through recognition of “eat-me” signals (e.g., phosphatidylserine, oxidized low-density lipoprotein, and ICAM3) by apoptotic cell binding opsonins (MFG-E8 and GAS6) and phagocytic receptors (such as CD36, MERTK, and α5β3 integrin); iii) the phagocyte engulfs the apoptotic corpse into an intracellular membrane-bound compartment termed the efferosome, where it is degraded.
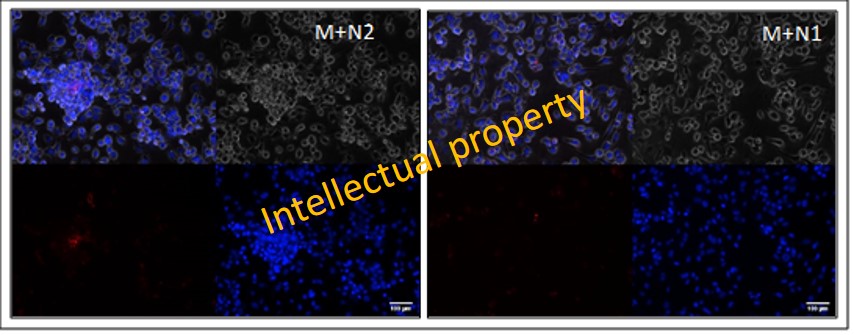
Figure 8. Representative immunofluorescent images of in vitro assessment of efferocytosis capacity of macrophages exposed to conditioned medium from N1 or N2 neutrophils. Scale bars = 100 μm
We have found increased gene expression of “eat-me” signals in macrophages exposed to N2 secretome, and as a result, an increased efferocytosis activity of these macrophages (Figure 8).
Within the Objective 2. Assess blockade of the PMN mediator S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) as a potential therapy to inhibit inflammation and promote cardiac repair post-MI”, during the period 2020-2021, we have developed and implemented histological and immunohistochemical methods to further investigate the effects of the treatment on the post-ischemic events occurring in the local environment of the myocardium. The results underlined that:
(i) 3 days ABR treatment significantly reduced the S100A9 presence in the myocardium 3 days after MI compared to untreated group. In addition, we demonstrate a statistically significant reduction of the fibrous myocardial tissue in the ABR-treated mice at 7 days after MI, mainly due to a reduction of the fibrotic process in the remote myocardium. Secondly, we show here for the first time that the 3 days S100A9 blockade promotes myocardial neovascularization.
(ii) S100A9 blockade with ABR-238901 inhibits hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and subsequently the myeloid cell production in the bone marrow (Figure 9), prevents myeloid cell migration from the bone marrow and spleen into the blood, and subsequently reduces the numbers of neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages in the infarcted myocardium. While the short-term blockade has positive effects due to lower degree of inflammation in the heart, the long-term blockade seems to impact myocardial repair.
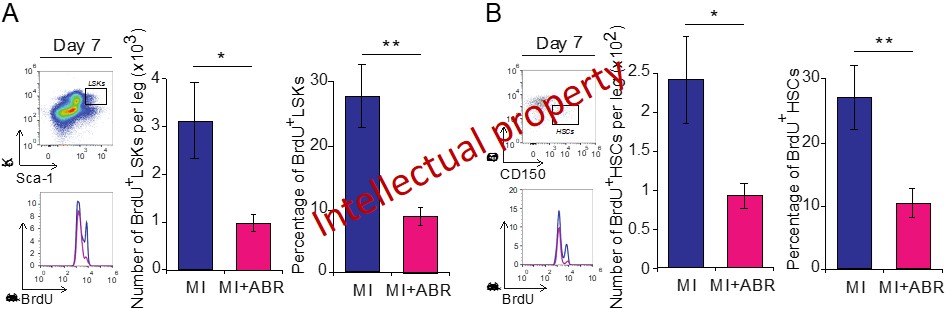
Figure 9. Numbers and proliferation of hematopoetic stem cells in the bone marrow on day 7 post-MI. (A) Gating strategy, histograms, numbers and percentages of proliferating BrdU+ cells within the Lin-Sca+Kit+ (LSK) cell population with and without ABR-238901 treatment on day 7 post-MI. BrdU was injected 24h prior to the analysis. (B) Gating strategy, histograms, numbers and percentages of proliferating BrdU+ Lin-Sca+Kit+CD150+CD48- hematopoetic stem cells (HSCs) in the bone marrow on day 7 post-MI.
(iii) S100A9 plays an important role in the transition from inflammatory monocytes to reparatory macrophages, both in-vitro and in-vivo in the post-ischemic heart. Long-term S100A9 blockade extended through the reparatory phase of the immune response reduces the numbers of reparatory macrophages in the heart by about 50%, leading to impaired myocardial recovery.
Within the Objective 3. Exploiting the immuno-modulatory properties of MSC to reduce inflammation and promote myocardial recovery post-MI, during 2020-2021 we focused on identifying the MSC-derived mechanisms involved in the polarization of macrophages and neutrophils into the reparatory M2/N2 phenotypes using a experimental design presented in the figure Figure 10.
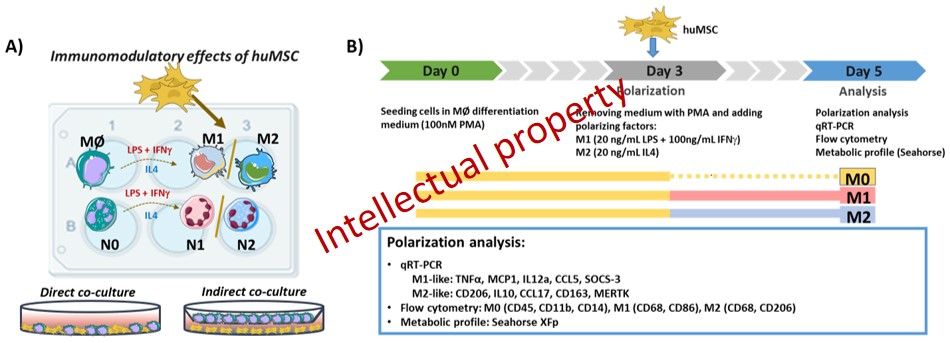
Figure 10. A) Schematic illustration of the in vitro experiments evaluating the immunomodulatory effects of MSC on the phenotypic polarization of Ma and PMN into the pro-inflammatory M/N1 or anti-inflammatory M2/N2 phenotypes. B) Detailed experimental design of the co-culture between MSC and THP-1-derived Mac.
Our results support the MSC’s ability to reduce the activation state of Mac in inflammatory conditions. Moreover, MSC were able to reprogram the metabolic phenotype of pro-inflammatory Mac from a glycolytic to a more energetic, mitochondrial-driven phenotype.
Importantly, MSC, through indirect-contact, were able to reduce the expression of the pro-inflammatory genes overexpressed in N1 neutrophils, and to upregulate the expression of anti-inflammatory genes CD206 and TGM2 in N2 neutrophils, indicating an N2-polarizing effect of MSC and imparting a N1-skewed phenotype to neutrophils.
In the Objective 4. Validate the clinical relevance of key innate immune mediators identified in Objectives 1-3 as potential biomarkers reflecting cardiac remodelling, prognosis, and response to treatment in patients with MI. we will examine the clinical relevance of innate immune mechanisms and their mediators for the prognosis of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients.
The purpose of this activity is to identify new prognostic biomarkers and potential treatment targets that can be applied in the clinical practice in the future. For this activity we will use two cohorts of ACS patients: a discovery cohort and a validation cohort recruited at the Emergency Hospital Bucharest (P2) and at Skane University Hospital Malmö, Sweden (P1).
Within the 2020 -2021 period, in order to verify the potential importance of S100A8/A9 as prognostic biomarker and potential mediator of heart failure in the ACS patients, we measured the plasma levels of the protein in the 524 patients included in the Swedish cohort and associated the values with the risk for incident heart failure (HF) during an average follow-up period of 2.5 years. We have also examined the correlations between plasma S100A8/A9 at the time of the MI and cardiac function measured by echocardiography at 1 year after the ischemic event in a sub-population of 113 patients where these data were available.
We found that patients with S100A8/A9 levels within the top tertile (T3) had a much higher risk to develop heart failure post-MI (Figure 11).
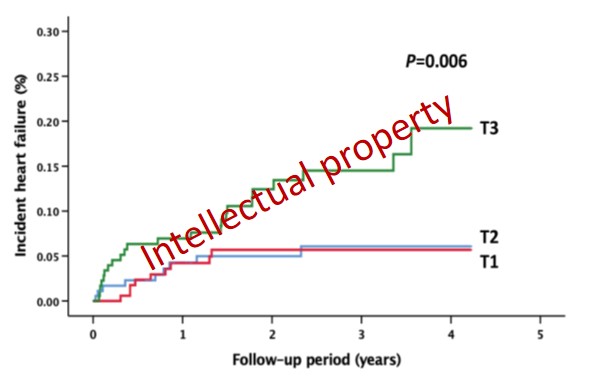
Figure 11. Incident heart failure post-ACS by baseline S100A8/A9 tertiles
Kaplan-Meier diagram of incident HF in the study population during follow-up, divided by baseline S100A8/A9 tertiles. P value for the trend, calculated with an unadjusted log-rank test.
In the 2021-2022 period, within the Objective 2 “Assess the blockade of the PMN mediator S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) as a potential therapy to inhibit inflammation and promote cardiac repair post-MI” (Fig 3), we have found that the short‐term pharmacological blockade of the pro‐inflammatory alarmin S100A9
- downregulates the expression of proteins involved in leukocytes recruitment and has important beneficial consequences on post‐ischemic myocardial repair and recovery;
- favorably modulates the levels of multiple anti‐apoptotic and pro‐apoptotic proteins involved in p53‐related pathways;
- maintains higher expression levels of cardiac structural proteins and inhibits several mediators previously found to drive abnormal compensatory cardiac recovery;
- reduces the markers of cardiac stress, such as NPM1, CSRP3, NPPA, TPT1 and NOL3.
These conclusions were demonstrated by performing high performance mass spectrometry analyses of the left ventricular proteome during the inflammatory and reparative phase, at 3- and 7-days post-MI, in mice with permanent myocardial ischemia induced by coronary artery ligation.
The bioinformatic analysis of the Gene Ontology Biological Process (GO BP) demonstrated enrichment of the regulation of the muscle cell apoptotic process, regulation of the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway and sarcomere organization at both day 3 and 7 post-MI. In addition, leukocyte cell–cell adhesion was significantly enriched on day 3 post-MI (Figure 12A, brown circle), while cardiac muscle hypertrophy was significantly enriched on day 7 post-MI (Figure 12B, yellow circle). According to the GO analysis, only 46 proteins out of the total differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) analyzed at the two time points were detected as being involved in the aforementioned biological processes. Figure 12 shows the relationship between these biological processes and the 46 proteins found to be differentially expressed after MI.
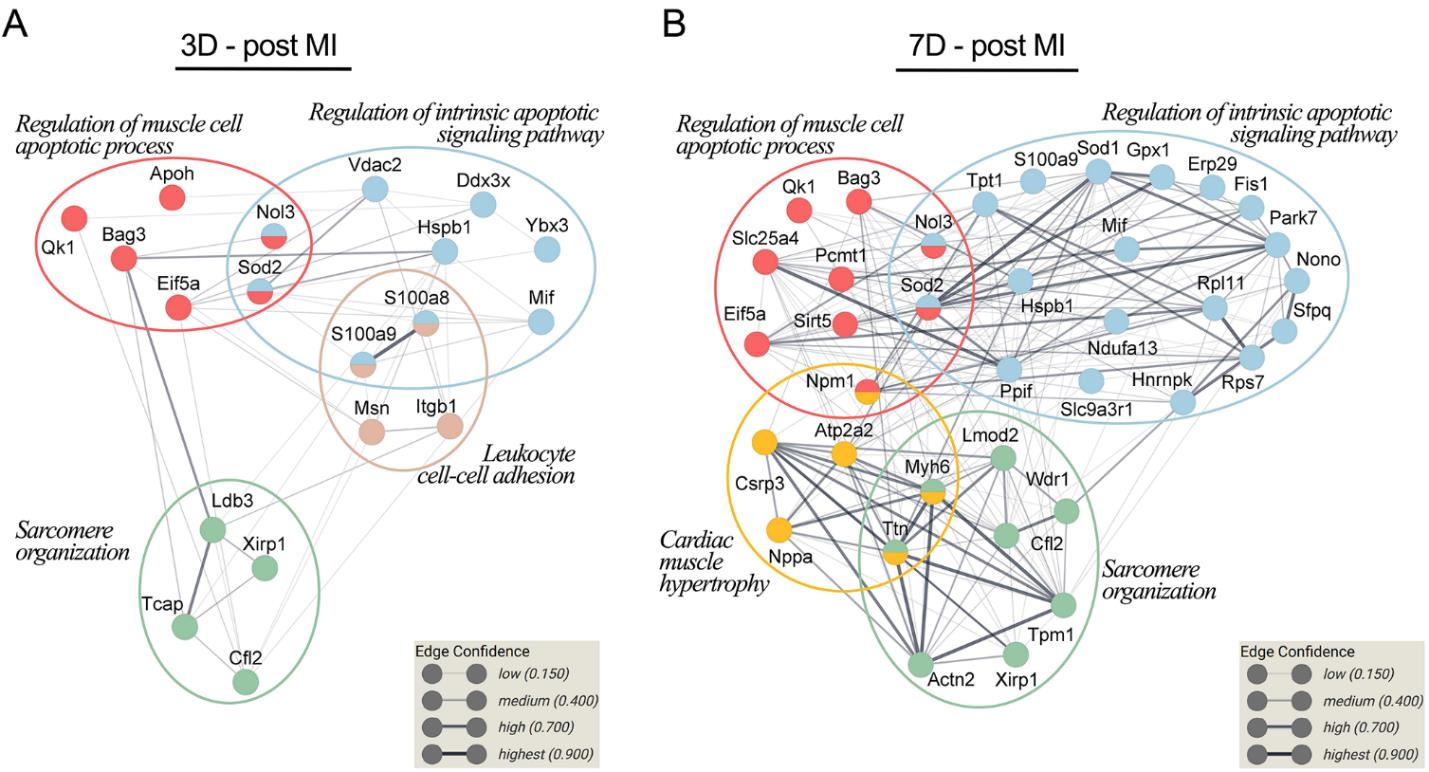
Figure 12. Associations between the biological processes related to ventricle repair and remodeling and differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) between the treatment groups. The protein–protein interaction networks at 3 days (A) and 7 days post-MI (B) were built using STRING 11.0. The proteins, identified by gene name, are represented as nodes. The thickness of the edge shows the strength of the interaction between two proteins (Boteanu et al., 2022)
We found that several proteins associated with the apoptotic processes were significantly altered in the MI groups at both 3- and 7-days post-MI, involved mainly in the regulation of the muscle cell apoptotic process and the regulation of the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. The GO BP enrichment analysis of DEPs at 3 days post-MI identified six proteins involved in the regulation of the muscle cell apoptotic process, while at 7 days post-MI we detected nine DEPs associated with the regulation of the muscle cell apoptotic process (Figure 13A). Similarly, at 3 days post-MI, we detected nine DEPs linked to the regulation of the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway, while at 7 days post-MI the analysis highlighted 19 DEPs involved in the regulation of the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway (Figure 13B). Concerning sarcomere organization, 4 proteins were statistically regulated at 3 days post-MI, while on the second time point, we observed 8 DEPs with altered spectral abundance.
To better highlight the effect of S100A9 inhibition at day 3 and 7 post-MI on these processes, we applied principal component-based multivariate statistics (PCA). The analysis performed on day 3 data did not reveal a clear differentiation of the proteome alterations between the MI and the MI + ABR groups (Figure 13D). However, PCA performed on day 7 post-MI samples revealed prominent differences among the quantitative features of the two groups, demonstrating that the protein content in LV from mice receiving ABR treatment was markedly closer to the two control groups (Ct, Sham) than to the MI animals (Figure 13E), which demonstrated a clear distancing and separation from all other groups.
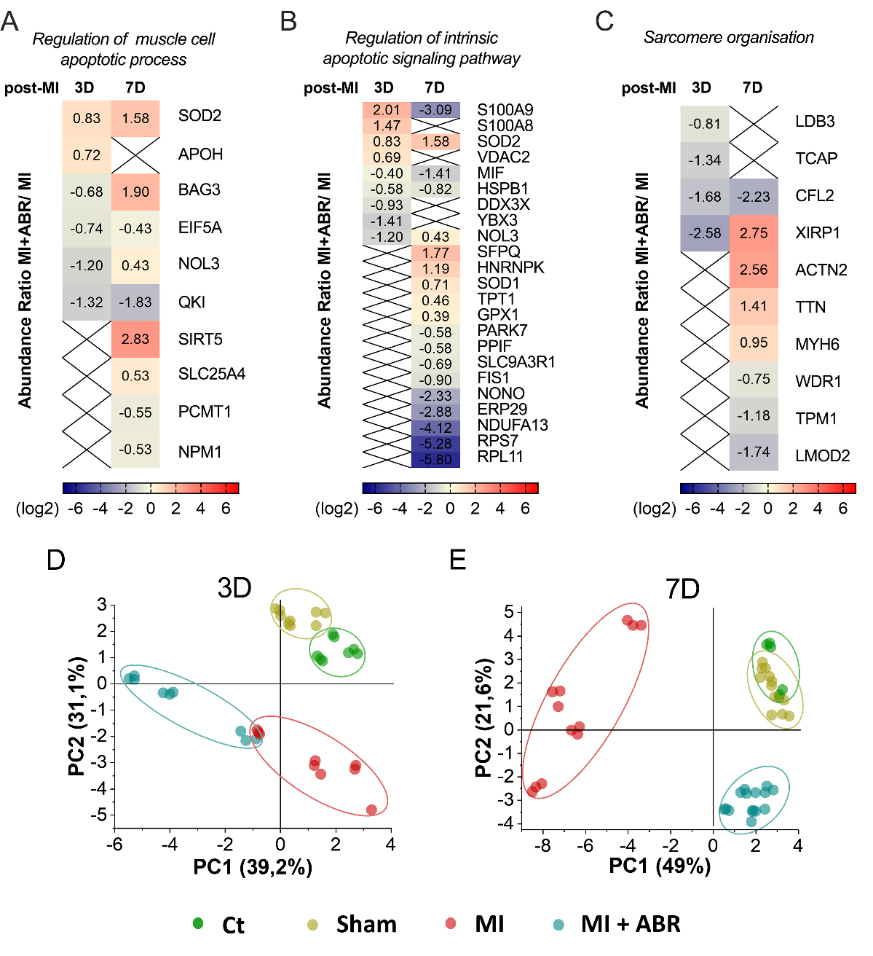
Figure 13. Heatmaps and principal component analysis (PCA) of the relative abundance of DEPs controlling biological processes involved in myocardial repair and remodeling. (A) DEPs involved in the regulation of the muscle cell apoptotic process, (B) regulation of the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway and (C) sarcomere organization. Red represents upregulated and blue represents downregulated proteins in the LV collected from the MI + ABR group compared to MI mice. Colored bars indicate the expression levels. PCA score plot based on the LC-MS/MS data of DEPs involved in the regulation of the muscle cell apoptotic process, regulation of the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway, and sarcomere organization GO BP for all experimental groups at 3 days (D) and 7 days (E) post-MI. An ellipse highlights the data points coming from one sample group. The colors of dots are: green, control (Ct) unoperated mice; dark yellow, Sham operated mice; red, MI mice; blue, MI + ABR mice. All protein short names are mentioned by the gene nomenclature guidelines (Boteanu et al., 2022).
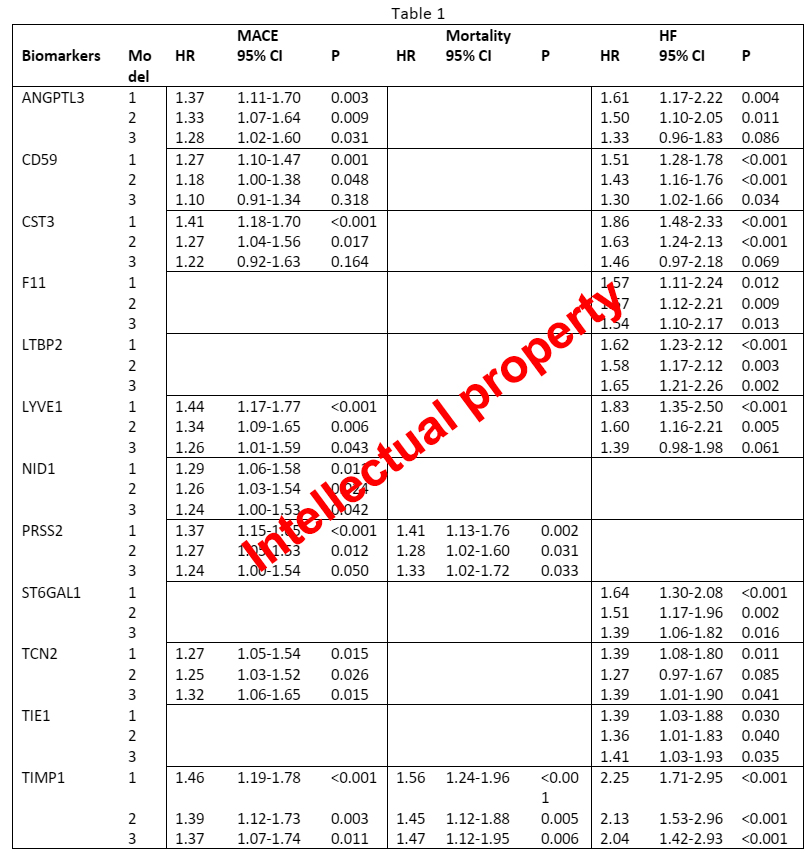
Within the Objective 4 “Validate the clinical relevance of key innate immune mediators identified in Objectives 1-3 as potential biomarkers reflecting cardiac remodelling, prognosis, and response to treatment in patients with MI”, we measured a large panel of immunometabolic mediators (the Cardiometabolic panel, OLINK, Uppsala, Sweden) in plasma samples collected at baseline and 6 weeks from the cohort of MI patients described above, and from a similar cohort of 550 MI patients recruited at Skane University Hospital in Malmö, Sweden, by Dr. Alexandru Schiopu (P1). By using Cox regression analysis models adjusted for potential clinical confounders, we examined the associations between biomarker values and prognosis, expressed as incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: incident MI or cardiovascular death), heart failure (HF) and mortality during follow-up.
We found that the baseline levels of NID1 (Nidogen 1) were significantly associated with the incidence of MACE. The F11 (Coagulation factor XI), LTBP2 (Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 2), ST6GAL1 (Beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1), and TIE1 (Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1) were associated with HF. ANGPTL3 (Angiopoietin-related protein 3), CD59 (CD59 glycoprotein), CST3 (Cystatin C), LYVE1 (Lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor 1), TCN2 (Transcobalamin 2) were associated with both MACE and HF. The PRSS2 (Trypsin-2) was associated with both MACE and mortality. TIMP1 (Metalloproteinase-inhibitor 1) was associated with all outcomes, independently of all confounders (Table 1). The hazard ratio (HR) is expressed per 1 standard deviation (SD) increase in biomarker values.
Dissemination:
Articles
1. Grauen Larsen H, Marinkovic G, Nilsson PM, Nilsson J, Engström G, Melander O, Orho-Melander M, Schiopu A. High Plasma sRAGE (Soluble Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products) Is Associated With Slower Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression and Lower Risk for First-Time Coronary Events and Mortality. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019 May;39(5):925-933. Impact factor: 6.64
2. Marinković G, Grauen Larsen H, Yndigegn T, Szabo IA, Mares RG, de Camp L, Weiland M, Tomas L, Goncalves I, Nilsson J, Jovinge S, Schiopu A. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory myeloid cell responses by short-term S100A9 blockade improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2019 Aug 21;40(32):2713-2723. Impact factor: 22.67
3. Vlad ML, Manea SA, Lazar AG, Raicu M, Muresian H, Simionescu M, Manea A. Histone Acetyltransferase-Dependent Pathways Mediate Upregulation of NADPH Oxidase 5 in Human Macrophages under Inflammatory Conditions: A Potential Mechanism of Reactive Oxygen Species Overproduction in Atherosclerosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Sep 2;2019:3201062. Impact factor: 4.82
4. Manea SA, Vlad ML, Fenyo IM, Lazar AG, Raicu M, Muresian H, Simionescu M, Manea A. Pharmacological inhibition of histone deacetylase reduces NADPH oxidase expression, oxidative stress and the progression of atherosclerotic lesions in hypercholesterolemic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice; potential implications for human atherosclerosis. Redox Biol. 2020 Jan;28:101338. Impact factor: 10.06
5. Grauen Larsen H, Yndigegn T, Marinkovic G, Grufman H, Mares R, Nilsson J, Goncalves I, Schiopu A. The soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products (sRAGE) has a dual phase-dependent association with residual cardiovascular risk after an acute coronary event. Atherosclerosis. 2019 Aug;287:16-23. Impact factor: 3.91
6. Preda MB, Lupan AM, Neculachi CA, Leti LI, Fenyo IM, Popescu S, Rusu EG, Marinescu CI, Simionescu M, Burlacu A. Evidence of mesenchymal stromal cell adaptation to local microenvironment following subcutaneous transplantation. J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(18):10889-10897. Impact factor: 4.86
7. Marinković G, Koenis DS, de Camp L, Jablonowski R, Graber N, de Waard V, de Vries CJ, Goncalves I, Nilsson J, Jovinge S, Schiopu A. S100A9 Links Inflammation and Repair in Myocardial Infarction. Circ Res. 2020 Aug 14;127(5):664-676. Impact factor: 17.36
8. Carmen Alexandra Neculachi, Livia Ioana Leti, Alexandrina Burlacu, Mihai Bogdan Preda Inflammation and Hypoxia Negatively Impact the Survival and Immunosuppressive Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells In Vitro. Romanian Journal of Cardiology | Vol. 31, No. 3, 2021. https://doi.org/10.47803/rjc.2021.31.3.547
9. Preda MB, Lupan AM, Neculachi CA, Leti LI, Fenyo IM, Popescu S, Rusu EG, Marinescu CI, Simionescu M, Burlacu A. Evidence of mesenchymal stromal cell adaptation to local microenvironment following subcutaneous transplantation. J Cell Mol Med. Sep;24(18):10889-10897, 2020. Impact factor: 4.86
10. Mihaila AC, Ciortan L, Macarie RD, Vadana M, Cecoltan S, Preda MB, Hudita A, Gan AM, Jakobsson G, Tucureanu MM, Barbu E, Balanescu S, Simionescu M, Schiopu A, Butoi E. Transcriptional Profiling and Functional Analysis of N1/N2 Neutrophils Reveal an Immunomodulatory Effect of S100A9-Blockade on the Pro-Inflammatory N1 Subpopulation. Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 10;12:708770. Impact factor: 7.56
11. Razvan Gheorghita Mares, Doina Manu, Istvan Adorjan Szabo, Mihaela Elena Tomut, Gabriela Pintican, Bogdan Cordos, Gabriel Jakobssons, Minodora Dobreanu, Ovidiu Simion Cotoi, Alexandru Schiopu. Studying the Innate Immune Response to Myocardial Infarction in a Highly Efficient Experimental Animal Model. Romanian Journal of Cardiology | Vol. 31, No. 3, 2021. https://doi.org/10.47803/rjc.2021.31.3.573
12. Boteanu RM, Suica VI, Uyy E, Ivan L, Cerveanu-Hogas A, Mares RG, et al. Short-Term Blockade of ProInflammatory Alarmin S100A9 Favorably Modulates Left Ventricle Proteome and Related Signaling Pathways Involved in Post-Myocardial Infarction Recovery. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 9;23(9):5289 – Impact Factor 6.208
Other manifestations:
✓ 35 participation to international/national conferences;
✓ > 10 oral presentations
✓ 2 phD thesis (in progress)
✓ We had numerous (monthly) partner meetings by zoom, mail, e-mail, or by direct contact
✓ 1 research internship between partners
A concluding Workshop entitled “Achievements and perspectives of INNATE-MI project” will be held on the 9th of December, 2022, at the ICBP “N. Simionescu” Institute, where the most notable achievements of the project will be presented to the interested public.

