National Grants
Project code: PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2019-2512
Contract number: 265PED/2020
Project title: Innovative triterpenes-based pharmacological strategy for the treatment of diabetes-associated micro- and macrovascular disorders – preclinical study
Acronym: THERDIAB
Project duration: 03/08/2020 - 28/10/2022
Project director: Dr. Simona-Adriana Manea
Abstract
Diabetes, a complex metabolic disorder, induces severely disabling and life-threatening micro- and macrovascular complications. Under current standards of care, the treatment of diabetic vasculopathies is challenging. Clinical and experimental reports (including ours) show that the dysregulation of vascular-specific signalling pathways in diabetes leads to the imprinting of a toxic long lasting hyperglycaemic memory contributing to micro-/macrovascular alterations. Thus, the development of advanced vascular-oriented therapies is needed. Evidence exists that triterpenes, a family of bioactive compounds produced by plants, could be highly effective anti-hyperglycaemic drugs in humans. Yet, the potential therapeutic role of triterpenes in diabetes-associated cardiovascular complications as well as the molecular basis of triterpenes action at the level of different vascular territories is largely unknown. The scope of this project is to develop a pharmacological strategy by implementing laboratory-validated biologically active triterpenes to reduce micro- and macrovascular disorders in diabetes. We hypothesize that triterpenes-enriched natural extracts or selective triterpenic acids may directly or indirectly regulate the expression and function of specific molecular targets (some validated by our group) that transduce the signals of diabetic factors to induce vascular remodelling and dysfunction. To confirm this hypothesis, we will employ original triterpenic acid-based formulations developed by our pharma partner (BIOTEHNOS SA), state-of-the art and complementary methodologies and in vitro and in vivo experimental models of diabetes. The expected primary outcomes are: (1) optimized technological protocol to obtain triterpenic acids in a highly purified and standardized state required for pharmaceutical applications; (2) experimentally validated triterpenes-based pharmacological strategy to reduce the progression of the micro- and macrovascular disorders in diabetes.
Objectives:
Objective 1. Development of innovative triterpenes-based formulations for enhanced pharmacological actions and minimal side-effects in diabetes-associated vascular disorders.
Objective 2. Preclinical testing and validation of the triterpenes-based pharmacological interventions to reduce micro- and macrovascular dysfunction in diabetes.
Dissemination:
Articles
1. Manea SA, Vlad ML, Rebleanu D, Lazar AG, Fenyo IM, Calin M, Simionescu M, Manea A. Detection of vascular reactive oxygen species in experimental atherosclerosis by high-resolution near-infrared fluorescence imaging using VCAM-1-targeted liposomes entrapping a fluorogenic redox-sensitive probe. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2021; 2021:6685612. doi: 10.1155/2021/6685612. Impact factor: 7.31.
2. Lazar AG, Vlad ML, Manea A, Simionescu M, Manea SA. Activated histone acetyltransferase p300/CBP-related signalling pathways mediate up-regulation of NADPH oxidase, inflammation, and fibrosis in diabetic kidney. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021; 10(9):1356. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091356. Impact factor: 7.765.
3. Manea SA, Vlad ML, Lazar AG, Muresian H, Simionescu M, Manea A. Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A contributes to atherosclerotic lesion formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by mediating oxidative stress and inflammation; evidence for implications in human atherosclerosis. Redox Biology, 2022. (Submitted). Impact factor: 10.787.
Oral communications at international meetings:
1. Manea SA, Vlad LM, Mares RG, Lazar AG, Preda BM, Schiopu A, Simionescu M, Manea A. Myeloid cell-derived S100A9 modulates the expression of histone methylation epigenetic enzymes in the myocardium after permanent ischemia in mice. Atherosclerosis. 2021, 331, e34.
2. Manea A, Vlad ML, Lazar AG, Manea SA. Focused ultrasound-induced targeted delivery of miR-155-5p inhibitor employing biomimetic microbubbles reduces NADPH oxidase expression and inflammation in atherosclerotic ApoE-/- mice. Cardiovascular Research, 2022, Vol. 118, Supplement 1, pg. cvac066. 197.
3. Manea A, Vlad ML, Lazar AG, Manea SA. SET7 methyltransferase mediates the up-regulation of NADPH oxidase expression and oxidative stress in the atherosclerotic aorta of apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.Virchows Archiv (2022) 481 (Suppl 1):S157.
Posters presented at national and international meetings:
1. Vlad LM, Manea SA, Mares RG, Lazar AG, Preda BM, Simionescu M, Schiopu A, Manea A. Pharmacological inhibition of the alarmin S100A9 reduces NADPH oxidase expression and oxidative stress in the infarcted myocardium in mice. Atherosclerosis. 2021, 331, e95-e96.
2. Lazar AG, Vlad LM, Olariu L, Manea SA, Manea A. Triterpenic acids inhibit the expression of inflammation-and oxidative stress-related markers in human pro-inflammatory macrophages. Atherosclerosis. 2021, 331, e79-e80.
3. Manea SA, Vlad LM, Lazar AG, Muresian H, Manea A. Inhibition of miR-155-5p reduces NADPH oxidase expression and oxidative stress in the aorta of hypercholesterolemic ApoE-deficient mice: potential implication in human atherosclerosis. FEBS OPEN BIO. 2021, 11, 141-142.
4. Lazar AG, Vlad LM, Manea A, Manea SA. Activation of histone acetyltransferase p300/CBP -dependent signaling pathways induces oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in the kidney of diabetic mice.38th Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology. 2021.
5. Vlad LM, Lazar AG, Manea SA, Manea A. Histone demethylase KDM5B mediates the up-regulation of pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory genes in M1-type macrophages. 38th Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology. 2021.
6. Manea SA, Lazar AG, Vlad ML, Manea A. Ursolic acid reduces inflammation and fibrosis in the kidney of diabetic mice. Cardiovascular Research, 2022, Vol. 118, Supplement 1, pg. cvac066. 225.
7. Lazar AG, Vlad ML, Manea A, Olariu L, Manea SA. Ursolic acid reduces NADPH oxidase expression and ensuing oxidative stress in diabetic kidney. Atherosclerosis, 2022, Vol. 355, pg. 206.
8. Vlad ML, Mares RG, Lazar AG, Manea SA, Preda BM, Simionescu M, Schiopu A, Manea A. Monocyte-derived macrophages mediate S100a8/A9-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in the ischemic myocardium. Atherosclerosis, 2022, Vol 355, pg. 268.
9. Manea SA, Vlad ML, Lazar AG, Manea A. miR-210-3p mediates the up-regulation of NADPH oxidase expression in the atherosclerotic aorta of hypercholesterolemic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice; potential implications for human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis, 2022, Vol. 355, pg. 49-50.
10. Manea A, Manea SA, Vlad ML, Lazar AG, Muresian H, Simionescu M. Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A mediates oxidative stress, inflammation, and atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice; prospective implications for human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis, 2022, Vol. 355, pg. 50.
11. Manea A, Vlad ML, Lazar AG, Manea SA. MicroRNA-210-3p contributes to inflammatory response in the atherosclerotic aorta of apolipoprotein E-deficient mice: potential role in human atherosclerosis. FEBS OPEN BIO, 2022, Vol. 12, pg. 152.
12. Manea SA, Lazar AG, Vlad ML, Manea A. Ursolic acid reduces NADPH oxidase expression and oxidative stress in the atherosclerotic aorta of apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by inhibiting NF-kB and STAT1/3 signaling. FEBS OPEN BIO, 2022, 12, pg. 151.
13. Manea SA, Lazar AG, Vlad ML, Manea A. Ursolic acid prevents the dysregulation in the expression of histone methylation-related epigenetic enzymes in diabetic kidney. Virchows Archiv (2022) 481 (Suppl 1): S86-S87.
14. Lazar AG, VladML, ManeaA, ManeaSA. Ursolic acid reduces inflammation and the development of atherosclerotic lesions in hypercholesterolemic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. International Conference and XXXIX Scientific Session of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 2022.
Results
Results - 2020
(1) Development of the concept and design of the functional model for the specificity and selectivity of the therapeutic agent depending on the biological structure of the target molecule; (2) Isolation and characterization of bioactive triterpenic acids of high purity from extracts of Salvia officinalis. Deliverable: Preliminary list of potential pharmacological targets of triterpenic acids validated in vitro. Dissemination: 1 article submitted for publication to an ISI journal with a high impact factor (Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity).
Results - 2021
(1) Development of the concept and design of the functional model for the specificity and selectivity of the therapeutic agent depending on the biological structure of the target molecule; (2) Isolation and characterization of high purity bioactive triterpenic acids from extracts of Salvia officinalis; (3) Selection of a panel of triterpenes as potential pharmacological agents in diabetes; (4) In silico analysis. Isolation and characterization of bioactive triterpenic acids of high purity from extracts of Salvia officinalis; (5) Determining the most efficient delivery route and optimal concentrations of triterpenic acids to obtain maximum therapeutic effects; (6) Correlation of the results obtained in vitro-in vivo for the prediction of pharmacological and toxicological effects; (7) Determination of the impact of triterpene-based treatment on the structural and functional changes of the renal artery and glomerular capillaries in the kidneys of diabetic mice; (8) Analysis of triterpene-induced modulatory effects on structural and functional changes in aortas of diabetic C57BL/6J mice. Deliverables: Standardized and laboratory-validated protocols to generate high-purity bioactive triterpenic acids from Salvia officinalis extracts. List of potential pharmacological targets of triterpenic acids. Pharmacological formulations optimized for increasing the systemic bioavailability of triterpenic acids in vivo. Triterpenic acids validated under laboratory conditions for improved pharmacological actions and minimal side effects in vivo. Dissemination: Articles: 2 articles published in ISI journals with high impact factor (Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, Impact Factor: 7.31 and Antioxidants, Impact Factor: 7.765). Oral communications at international scientific events: 1. Posters presented at national and international scientific events: 5.
Results - 2022
(1) Development of experimental animal models with diabetes and atherosclerosis; (2) Determination of the impact of triterpene-based treatment on the structural and functional changes of blood vessels in the kidneys of diabetic mice; (3) Determination of the impact of treatment with triterpenic acids on the formation and evolution of atherosclerotic lesions in ApoE-/- mice; (4) Determination of the impact of pharmacological interventions on certain plasmatic metabolic parameters in the blood of experimental animals. Deliverables: Validated experimental laboratory models of diabetes and atherosclerosis for testing the therapeutic effects of triterpenic acids. Preclinically validated procedure based on triterpenic acids to reduce microvascular dysfunction induced by diabetes. Preclinically validated therapeutic strategy based on triterpenic acids to reduce the structural and functional changes associated with diabetes in the large blood vessels. Preclinically validated pharmacological intervention based on triterpenic acids to reduce the progression of atherosclerotic lesions. Experimentally validated report on highlighting the modulatory effects of triterpenic acids on systemic metabolic parameters. Preclinically validated report on the potential beneficial effects of triterpenic acids on the structure and function of different organs. Pharmacological interventions based on preclinically validated triterpenic acids to reduce microvascular dysfunction in diabetes. Dissemination: Articles: 1 manuscript submitted for publication in an ISI journal with a high impact factor (Redox Biology, Impact Factor: 10.787); 2 manuscripts in preparation. Oral communications at international scientific events: 2. Posters presented at international scientific events: 9
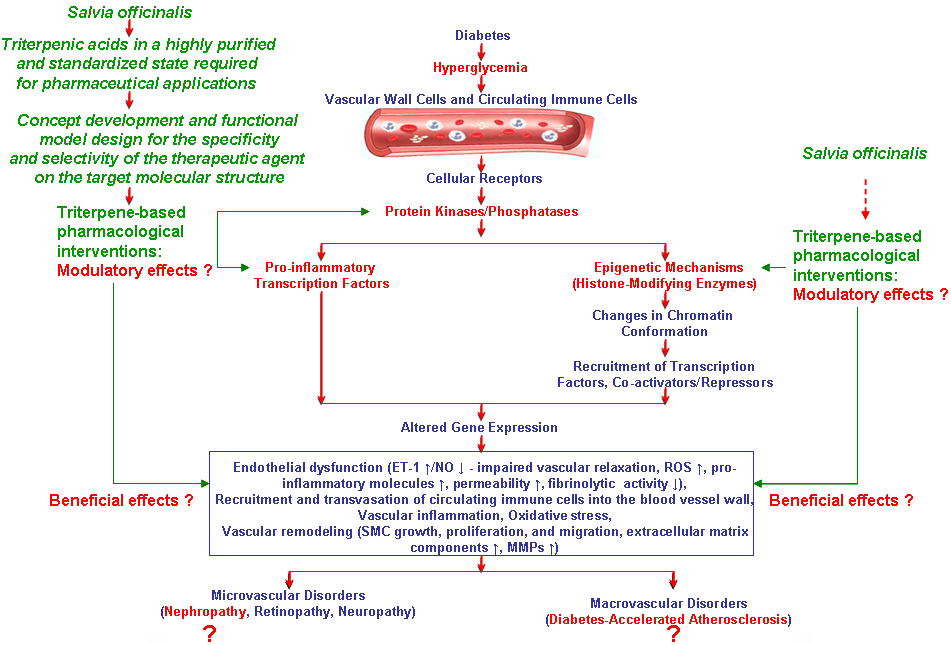
Figure 1. Experimental strategy to investigate the potential therapeutic targets of triterpenic acids in diabetes-associated micro- and macrovascular complications.
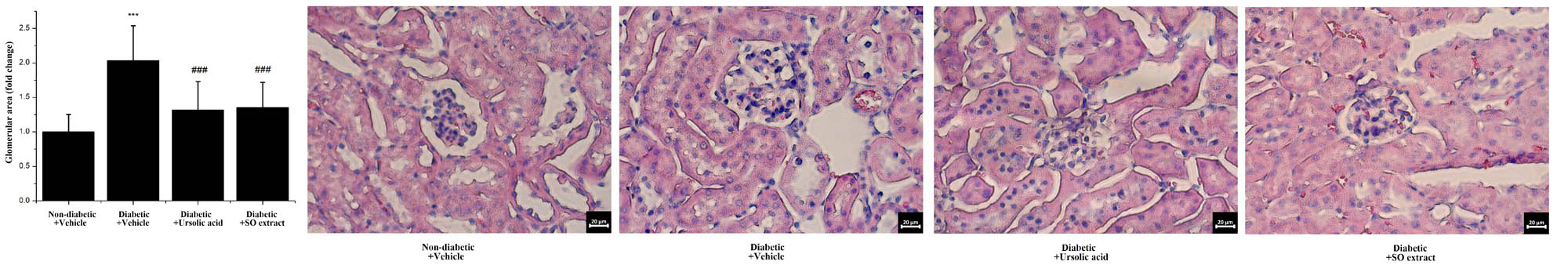
Figure 2. Treatment of diabetic mice with ursolic acid or Salvia officinalis extract containing 90.7 % ursolic acid and 5.8% oleanolic acidreduces glomerular hypertrophy.

