National Grants
| PHASE IV |  |
Project ID: PN-II-PT-PCCA-2011-3.1-0184
Contract: PCCA 127/2012-2016
Project title: „New predictive biomarkers for the evolution of the stable and unstable coronary artery disease identified by lipidomic, proteomic and molecular biology technologies” (BIOMARCAD)
Titlul proiectului: „Noi biomarkeri predictivi pentru evoluţia bolii coronariene, stabile şi instabile, identificaţi prin tehnologii de lipidomică, proteomică şi biologie moleculară” (BIOMARCAD)
Contract autority: Executive Unit for Financing Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation
- Joint Applied Research Projects Program (Unitatea Executivă pentru Finanţarea Învăţământului Superior, a Cercetării, Dezvoltării şi Inovării – UEFISCDI)
Partners CO: Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology „Nicolae Simionescu”, Bucharest
P1: Elias Emergency University Hospital, Bucharest
Project manager: Anca V. SIMA, Ph.D., Associate member of the Romanian Academy
Partner manager P1: Andreea-Catarina POPESCU, M.D., Ph.D.
|
CO Team Camelia S.Stancu, Ph.D. Loredan S. Niculescu, Ph.D. Gabriela M. Sanda, Ph.D. Laura Toma, Ph.D. Mariana Deleanu, Dipl. Chem. Ing. Elena Constaninescu, Ph.D. Horia Maniu, Ph.D. Natalia Simionescu, Ph.D. student Andrei Constantinescu, Ph.D. student Mihaela G. Carnuta, Master student Daniela Rogoz, Assistant Cristina Dobre, Assistant Camelia Matei, Assistant |
P1 Team Roxana M. Popescu, M.D., Ph.D. Adelina Vlad, M.D., Ph.D. Simona Petrescu, M.D., Ph.D. |
FUNDS
Year |
Funds |
2012 |
623.000 |
2013 |
386.400 |
2014 |
415.800 |
2015 |
208.111 |
Total |
2.000.000 |
Summary
Coronary artery disease (CAD), the leading cause of mortality and loss of productive life years worldwide, is generated mainly by atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial blood vessels. Although the minute pathobiological alterations occurring in atherosclerosis have been revealed, the fight against this disease is hampered due to the shortage of early signs, such as biomarkers with prognostic value for the evolution of atherosclerosis and the ensuing CAD. To cover this gap, the goal of this project is to establish new biomarkers with potential to predict the risk for developing life-threatening events in CAD patients, and to test the relevance of the measured biomarkers in patients by correlating them with the clinical evolution of CAD. A complex experimental setting will include clinical and experimental research performed by a consortium of two partners with recognized achievements in their respective fields. The novelty of the project is the detection of oxidized lipid molecules, translational regulatory molecules (miRNAs) and inflammatory molecules, the establishment of a link between the effect of oxidized lipids on the cellular secretion of miRNAs, pro-inflammatory molecules and on the switch of monocytes to the inflammatory phenotype by the use of cultured human endothelial cells and monocytes, and the correlation between circulating endothelial progenitor cells and the inflammatory monocytes from the CAD patients’ blood. The originality of the project resides in the final design of a protocol using a group of biomarkers implicated in the three pathways of atherosclerosis (lipid oxidation, transcriptional regulation and inflammation) that have the potential to predict CAD evolution and the transfer of the methodology for detection of the new biomarkers from bench to the clinic, to allow, at reasonable cost, the early prediction of life-threatening events, which will lead to a prolongation of the lifespan.
Rezumatul proiectului
Afectiunile coronariene, cauza principala de mortalitate si de diminuare a calitatii vietii la nivel mondial, sunt generate in majoritatea cazurilor de ateroscleroza, o boala inflamatorie cronica a arterelor. Desi alterarile patobiologice care se produc in ateroscleroza sunt cunoscute, lupta impotriva acestei boli este impiedicata de lipsa semnalelor timpurii, cum ar fi biomarkerii cu valoare prognostica pentru evolutia aterosclerozei si afectiunilor coronariene ulterioare. Pentru a completa acest gol, scopul acestui proiect este de a stabili noi biomarkeri cu potential predictiv pentru riscul de aparitie a evenimentelor critice ce pun in pericol viata pacientilor cu afectiuni coronariene si de a testa relevanta biomarkerilor propusi prin corelarea lor cu evolutia clinica a afectiunilor coronariene. O abordare experimentala complexa va include cercetari clinice si experimentale realizate de un consortiu alcatuit din doi parteneri cu experienta recunoscuta in domeniul fiecaruia de activitate. Noutatea acestui proiect este reprezentata de detectarea moleculelor lipidice oxidate, moleculelor de reglare transcriptionala (microARN) si moleculelor inflamatorii cu valoare predictiva, stabilirea unei legaturi intre lipidele oxidate si secretia celulara de microARN si de molecule pro-inflamatorii, precum si efectul asupra tranzitiei monocitelor spre un fenotip inflamator prin utilizarea celulelor endoteliale si monocitelor umane cultivate si corelatia dintre celulele endoteliale progenitoare circulante si monocitele inflamatorii din sangele pacientilor cu afectiuni coronariene. Originalitatea proiectului consta in elaborarea unui protocol final utilizand un grup de biomarkeri implicati in cele trei cai de stimulare a procesului aterosclerotic (oxidarea lipidica, reglare transcriptionala si inflamatie) si transferul metodologiei de masurare a noilor biomarkeri din laborator in clinica („from bench to the clinic”), pentru a permite, cu costuri rezonabile, predictia timpurie a evenimentelor critice ce pun in pericol viata pacientilor, ceea ce va conduce la o crestere a duratei de viata.

Schematic representation of the working hypothesis. The present project proposes to validate new biomarkers with predictive potential for the evolution of CAD by following three distinct pathways. In hyperlipidemia related CAD, phospholipids and fatty acids from circulating lipoproteins suffer oxidative modifications generating reactive species such as HPETE, HPODE, or 4-HDDE which we propose as predictive biomarkers for the evolution of stable and unstable angina (the oxidized lipids pathway). These aggressive oxidized lipids may induce an inflammatory response in the cells of the arterial wall (ex. endothelial cells) or circulating inflammatory cells (monocytes). The inflammatory component of CAD will be evaluated by measuring soluble molecules (VAP-1, IL-33, DPP4, MMP-14) proposed as new biomarkers with prognostic value (the inflammatory pathway). The communication between endothelial cells and inflammatory cells is proposed to be regulated, at least in part, by microRNAs (miR-21, miR-33, miR-10a, miR-125-5p, miR-146a) that can be found intracellularly or secreted in the circulation and which are considered a new class of biomarkers (the transcription regulatory pathway). Validation of these new predictive biomarkers will be made on in vitro experimental models (expression, secretion by EC and monocytes) and by transferring all the laboratory data to the clinic in order to be correlated with CAD evolution along the three years of the project.

The workflow of the project. The project moves essentially from a screening and clinical profiling phase of CAD patients, via a process of experimental evaluation, towards the validation of new biomarkers as predictive parameters. Importantly, during the maturation of the program, it is planned that human and cellular model studies will in turn provide additional mechanistic information. The arrows in the diagram reflect this analysis process of new biomarkers and the possible correlation between different class of parameters.
General objective
The goal of this project is to establish new biomarkers with potential to predict the risk for developing life-threatening events in CAD patients, and to test the relevance of the measured biomarkers in patients, by correlating them with the evolution of CAD. The project has four specific objectives as follow:
Objective 1. Measurement of oxidized lipids and dysfunctional lipoproteins in the blood of patients with stable or unstable CAD.
Objective 2. Determination of specific microRNAs (miRNAs) and inflammatory molecules in the plasma of CAD patients with SA, UA or MI.
Objective 3. Setting up of an in vitro experimental model to evaluate the effect of CAD patients sera on the production of inflammatory biomarkers by cultured endothelial cells and monocytes-macrophages; assessment of circulating EPC and monocytes.
Objective 4. Validation of the predictive potential of the identified biomarkers for the CAD evolution; to establish the transfer of methodology for detection of the new biomarkers in the clinic laboratory.
Obiectivul general
Scopul acestui proiect este de a stabili noi biomarkeri cu potential predictiv pentru riscul de aparitie a evenimentelor critice ce pun in pericol viata pacientilor cu afectiuni coronariene si de a testa relevanta biomarkerilor masurati la pacienti prin corelarea lor cu evolutia clinica a afectiunilor coronariene. Proiectul are patru obiective specifice, dupa cum urmeaza:
Obiectiv 1. Masurarea lipidelor oxidate si a lipoproteinelor disfunctionale din sangele pacientilor cu afectiuni coronariene stabile sau instabile.
Obiectiv 2. Determinarea microARN specifici si moleculelor inflamatorii in plasma pacientilor cu afectiuni coronariene cu angina stabila (AS), instabila (AI) sau infarct miocardic (IM).
Obiectiv 3. Elaborarea unui model experimental in vitro pentru evaluarea efectelor serurilor provenite de la pacienti cu afectiuni coronariene asupra productiei de biomarkeri inflamatorii de catre celulele endoteliale si monocite-macrofage cultivate; evaluarea celulelor endoteliale progenitoare si monocitelor circulante.
Obiectiv 4. Validarea potentialului predictiv a biomarkerilor identificati pentru evolutia afectiunilor coronariene; realizarea transferului metodologiei de detectie a noilor biomarkeri in laboratorul clinic.
Phase I (2012)
Title: Identification of putative biomarkers with prognostic value in the blood of patients with stable angina (SA), unstable angina (UA) or myocardial infarction (MMI): oxidized lipids and dysfunctional lipoproteins.
Period: 03 July 2012 – 5 December 2012
Objective: Measurement of oxidized lipids and dysfunctional lipoproteins in the blood of patients with stable or unstable CAD.
Task 1.1. Enrollment of patients, ECG, echocardiography, ECG stress test (for those with only risk factors), ultrasound examination of cervico cerebral arteries (Doppler exam) (P1).
Task 1.2. Blood collection and current biochemical analysis (glucose, creatinine, cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, troponin, CK, CKMB, AST, ALT, LDH) in CAD patients plasma (P1).
Task 1.3. Follow-up of all patients at 3 months (M3) and 6 months (M6) (P1).
Task 1.4. Measurement of lipid-related markers levels for oxidative stress in plasma of CAD patients: 4-HDDE, HPETE, HPODE (CO).
Task 1.5. Analysis of HDL from CAD patients: particle size and lipid characterization (fatty acids, 4-HDDE, HPETE, HPODE, oxidized phospholipids) and pre-β1-HDL measurement (CO).
Task 1.6. Statistical analysis of the correlation between plasma lipid biomarkers levels and clinical status of CAD patients (CO, P1).
Principal results obtained during the Phase I (03.07-31.12.2012)
The objective of this first phase of the study was the identification of biomarkers with prognostic value in the blood of patients with stable or unstable angina, myocardial infarction: oxidized lipids and dysfunctional lipoproteins. The analysis was done on blood and urine of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD): unstable angina (UA), acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and one month after inception of myocardial infarction (MMI) and stable angina (SA), as compared to subjects at risk for CAD without cardiac events (HR) and healthy subjects (C).
After analyzing the data obtained during the first phase of BIOMARCAD project, the following partial conclusions were drawn:
- Average plasma level of 15(S)-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid [15(S)-HETE] and 13(S)-hydroxy-octadecadienoic acid [13(S)-HODE)] in UA patients is higher compared to SA patients.
- There is a tendency for plasma 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) level to be increased in UA vs SA and thus be considered as potential biomarker to predict CAD evolution.
- Average level of serum phospholipids is higher in UA patients.
- Average levels of plasma LDL-cholesterol, apoB and apoE are significantly higher in UA patients compared to SA patients.
- Average level of oxidized LDL in plasma of UA patients is significantly higher compared to SA patients. Oxidized LDL is positively correlated with total cholesterol, triglycerides, phospholipids, LDL-cholesterol, apoB-100 and apoE levels and CETP activity.
- Average level of plasma HDL-cholesterol is lower in UA patients compared to SA and control groups.
- The activity of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) is significantly higher in plasma of UA patients compared to SA and control groups.

Figure 1. Boxplot distributions of plasma and urine 4-HNE, plasma and urine 15-HETE, plasma 13-HODE and oxidized LDL in studied groups. Data were analysed by using SPSS 21 software. Boxplots contain median value, standard deviation and 95% confidence interval box for all individual variables analysed. Differences between the individual groups were examined with One-Way Anova test and Posthoc LSD analysis.
- Plasma lipoproteins were separated by fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) technique and their analysis of the obtained fractions showed a shift of LDL peak to smaller atherogenic particles for SA and further for UA patients compared to control subjects. LDL particles from SA and UA patients have an increased cholesterol concentration compared to LDL from control subjects. HDL peak was shifted to smaller particles for SA and UA patients compared to control subjects. The cholesterol concentration of HDL particles decreased in SA and UA patients compared to control subjects.

Figure 2. Plasma FPLC profile of lipoproteins separated from HR subjects and from SA, UA and AMI patients.
- We established an original protocol for HDL isolation and analysis: to characterize HDL functionality, we combined some techniques in order to obtain information regarding HDL biochemical composition and physical properties (size) by using a minimal volume of plasma (200 µl).
- The principal difficulty to obtain relevant results was due to the extensive treatment of the studied patients with statins, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers (absolutely necessary for the clinical success).
In conclusion, the clinical and biochemical data resulted in the First Phase of BIOMARCAD study confirm the integral fulfilment of the objectives and tasks proposed in the contract PCCA 127 in 2012.
Phase II (2013)
Title: Identification of circulating microRNA and inflammatory molecules in the blood of patients with stable angina (SA), unstable angina (UA) or myocardial infarction (MMI).
Period: 01 January 2013 – 31 December 2013
Objective: Measurement of specific miRNA and inflammatory molecules in the blood of CAD patients with stable and unstable atherosclerotic plaques.
Task 2.1. Follow-up of all patients at 12 months (M12); blood collection, clinical and biochemical analysis (P1).
Task 2.2. Measurement of non-coding-RNA (micro-RNA) with functional targeting capabilities involved in cellular lipid metabolism (miR-33a, miR-125a-5p) and endothelial inflammation (miR-10a, miR-21, miR146-a) from CAD patients’ plasma (CO).
Task 2.3. Measurement of new inflammatory stress biomarkers levels in plasma of CAD patients: soluble chemokines (sVAP-1) and matrix metallo-proteases (MMP-14) (CO).
Task 2.4. Analysis of the statistical relevance of the new biomarkers measured above with the statistical relevance of known biomarkers of CAD (e.g. hsCRP, troponin, CKMB, IL-1β, sVCAM-1, sMCP-1, oxLDL, auto-antibodies against oxLDL, MMP-2/9) (CO, P1).
Task 2.5. Dissemination of the results – national and international mobility.
Principal results obtained during the Phase II (01.01-31.12.2013)
The objective of the second stage (2013) of the PCCA 127 project was to identify circulating non-coding-RNA (miRNA) and some inflammatory markers in the blood of stable angina (SA), unstable angina (UA), acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and one month after inception of myocardial infarction (MMI) patients, as compared to subjects at risk for CAD without cardiac events (HR) and healthy subjects (C).
After analyzing the data obtained during the second phase of BIOMARCAD project, the next partial conclusions were drawn:
- after 1-year, evaluation of studied patients showed a significant improvement of their plasma lipid profile (lower serum lipids and apolipoproteins levels), a decrease of the oxidative stress (lower plasma 4-HNE levels and increasing PON1 activity) and inflammatory status (lower serum IL-1β levels);
- PCR array profiling of 84 circulating miRNA (screening) in patients’ sera identified 3 miRNA with the highest normalized levels (fold change) relative to controls (miR-122a, miR-92a and miR-486a);
- protocols for miRNA, sVAP-1 and MMP-14 analysis were established;
- 6 individually analyzed miRNA (miR-122a, miR-92a, miR486a, miR-125a, miR-146a, miR-33a) presented increased serum concentrations in HR, SA, UA, MMI and AMI patients as compared to control subjects (Figure 1).
- miR-486a showed the highest serum concentrations from the 6 miRNA analyzed, data from literature showing that miR-486a is associated with the cardiomyocytes function;
- circulating miR-486a and miR-92a (known to be associated with endothelial dysfunction) were increased in MMI patients’ sera as compared to UA group;
- circulating miR-125a, miR-146a and miR-33a did not differ between the patients groups.

Figure 1. Boxplots distribution of serum miRNA levels (miR-486a, miR-92a, miR122a, miR125a, miR146a, miR33a) in the studied groups. Measurements were done with TaqMan miRNA assay (Applied Biosystems, Life Technologies, USA).
- plasma sVAP-1 levels significantly increased in MMI patients as compared with UA group.
- plasma MMP-14 levels did not differ between SA and UA patients, as well as between UA and MMI groups.

Figure 2. Boxplots distribution of plasma soluble chemokines (sVAP-1) and matrix metalloproteases (MMP-14) in the studied groups. Measurements were done with a kit from R&D Systems, Germania (VAP-1) or by Western blot method using a monoclonal antibody from Abcam, UK (MMP-14).
The 45% budget cutoff in 2013 affected the planned activity, reducing the number of proposed biomarkers (DPP4, sIL33, sST2) and the number of analyzed samples (plasma PLA2 activity, VAP-1 and MMP-14 levels), as well as the individual analysis of some microRNA with predictive potential (that were restrained to a smaller number than necessary for the individual validation); some activities were re-planned for the next stages of the project, hoping that the funds reduced in 2013 will be reallocated in 2014, an absolutely necessary condition for the validation and confirmation of the obtained results and their successful publication in ISI journals.
The principal difficulty in obtaining relevant results was due to the extensive treatment of the studied patients with statins, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers (definitely necessary for the successful treatment).
The dissemination of the 2013 results consisted in 4 articles published or under review for publication in ISI-ranked journals (cumulative ISI impact factor: 7.34), 18 communications, as invited speaker or with poster at international and national scientific meetings; we stress that all articles and communicated papers have mentioned the funding from PCCA127 project.
In conclusion, the obtained clinical and biochemical data, as well as the number of papers published in ISI-ranked journals and/or communicated at international and national scientific meetings in the Second Phase of BIOMARCAD study confirm the integral fulfilment of the objectives and tasks proposed in the contract PCCA 127 (and the Addendum 1/2013) for the year 2013.
Dissemination activities
Scientific articles
Niculescu L.S., Sanda G.M., Sima A.V., HDL inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress by stimulating apoE and CETP secretion from lipid-loaded macrophages, Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun.,434, 173–178, 2013 (ISI IF 2,406).
Stancu C.S., Sanda G.M., Deleanu M., Sima A.V., Probiotics determine hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects, Mol. Nutr. Food Res., DOI 10.1002/mnfr.201300224, 2013 (ISI IF 4,31).
Niculescu L.S., Sanda G.M., Simionescu N., Sima A.V., Bilberries exert an anti-atherosclerotic effect in lipid-loaded macrophages, Cent. Eur. J. Biol., DOI: 10.2478/s11535-013-0268-8, 2013 (ISI IF 0,818).
Simionescu N., Niculescu L.S., Sanda G.M., Margina D., Sima A.V. Identification of circulating microRNA that are specifically increased in hyperlipidemic and/or hyperglycemic hypertensive patients sera. Submitted Clin. Chem. Lab. Med (ISI IF 3,009).
International Scientific Meetings
Oral communication
Niculescu L.S., Sima A.V. Analysis of circulating micro-RNA using real-time PCR; technique and challenges. Oral communication in Sesiunea Plenara IV „Modern Techniques of Cellular and Molecular Biology” at The 5th International Congress and 31st Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Scoiety for Cell Biology, Timişoara, 5-9 iunie 2013
Poster communications
Simionescu N., Niculescu L.S., Sanda G.M., Margina D., Sima A.V. Analysis of micro-RNA biomarkers in serum of subjects with hyperlipidemia and/or hyperglycemia. The 5th International Congress and 31st Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Scoiety for Cell Biology, Timişoara, 5-9 iunie 2013.
Niculescu L.S., Sanda G.M., Simionescu N., Rogoz D., Sima A.V. Bilberries exert an anti-atherosclerotic effect regulated by NF-κB and PKA pathways in human lipid-loaded macrophages. The 5th International Congress and 31st Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Scoiety for Cell Biology, Timişoara, 5-9 iunie 2013
Niculescu L.S., Simionescu N., Popescu A.C., Popescu R.M., Dimulescu D.R., Sima A.V. Analysis of micro-RNA Biomarkers in Plasma of Coronary Heart Disease Patients. The 5th International Congress and 31st Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Scoiety for Cell Biology, Timişoara, 5-9 iunie 2013.
Stancu C.S., Sanda G.M., Deleanu M., Rogoz D., Sima A.V. Probiotics determine hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects in hyperlipidemic hamsters. The 5th International Congress and 31st Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Scoiety for Cell Biology, Timişoara, 5-9 iunie 2013.
Stancu C.S., Deleanu M., Popescu A.C., Popescu R.M., Dimulescu D.R., Simionescu M., Sima A.V. Oxidized lipids as potential biomarkers for the coronary artery disease. The 5th International Congress and 31st Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Scoiety for Cell Biology, Timişoara, 5-9 iunie 2013.
Deleanu M., Gabriela M. Sanda, Camelia S. Stancu, Anca V. Sima, Characterization of LDL modified by oxidation or glycation. The 5th International Congress and 31st Annual Scientific Session of the Romanian Scoiety for Cell Biology, Timişoara, 5-9 iunie 2013.
Munteanu A., Popescu M., Isvoranu G., Suciu L., Marinescu B., Pavel B., Zagrean L. Delayed Sevoflurane Preconditioning Enhances Endothelial Progenitor Migration in the Ischemia/Reperfusion (I/R) Injured Myocardium. Experimental Biology 2013, 20–24 April 2013, Boston, USA.
National Scientific Meetings
Invited speaker
Simionescu M., Sima A.V. Stilul de viaţă şi bolile cronice netransmisibile: date celulare şi moleculare, Al doilea Congres Naţional „Bolile cronice netransmisibile”, Bucureşti, 8-9 februarie 2013.
Simionescu M, Sima A. V. State of the art lecture: Aspecte moleculare ale alimentaţiei sănătoase, A Treia Conferinţă Naţională Sănătate Prin Alimentaţie Bucureşti, 26 octombrie 2013
Simionescu M, Sima A. V. State of the art lecture: Bazele moleculare ale sindromului metabolic, A Iv-A Conferinţă Managementul Dislipidemiilor, al Obezităţii si Sindromului Metabolic, 22-23 Noiembrie 2013.
Dimulescu D. Diagnostic și prognostic în boala coronariană stabilă. Congresul Național de Cardiologie, Sinaia 3-05.10.2013
Dimulescu D. Riscul hemoragic și managementul sângerării. Congresul Național de Cardiologie, Sinaia 3-05.10.2013
Dimulescu D. Ce aduce nou „Ghidul de Diabet, Pre-diabet şi Boli Cardiovasculare”, Congresul Național de Cardiologie, Sinaia 3-05.10.2013
Dimulescu D., N. Hâncu. Diabetul zaharat şi boala cardiovasculară: dezamorsarea unei bombe! Mesaje de luat acasă: opinia cardiologului şi a diabetologului. Congresul Național de Cardiologie, Sinaia 3-05.10.2013
Dimulescu D. Protecția vasculară în hipertensiunea arterială: dincolo de cifre. Conferinta Nationala a Grupurilor de Lucru, Brasov, 16-18.05.2013
Dimulescu D. Dispnee acută și durere toracica. Conferinta Nationala a Grupurilor de Lucru, Brasov, 16-18.05.2013
Dimulescu D. Tratamentul cu statine la pacientul vascular acut. Conferinta Nationala a Grupurilor de Lucru, Brasov, 16-18.05.2013
Title: Setting up of an in vitro experimental model to evaluate the effect of the sera of CAD patients on the production of inflammatory molecules by cultured endothelial cells and macrophages; evaluation of circulating monocytes
Period: 01 January 2014 – 31 December 2014
Objective: To evaluate in vitro the effect of CAD patients’ sera on the production of the identified biomarkers by cultured endothelial cells and macrophages; assessment of circulating monocytes.
Task 3.1. Follow-up of all patients at 24 months (M24); blood collection, clinical and biochemical analysis (P1).
Task 3.2 Evaluation of miRNAs associated with lipoproteins from CAD patients’ plasma (CO).
Task 3.3. Quantification of patients’ sera inflammatory potential by measuring the induced secretion of miRNAs, sVAP-1, sIL-33 and MMP-14 by cultured human macrophages; immunolocalization of cellular VAP-1, IL-33 and MMP-14 (CO).
Task 3.4. Quantification of the CAD patients’ sera regulatory potential related to miRNA processing machinery (Drosha/DGCR8, Dicer) in cultured THP-1 macrophages (CO).
Task 3.5. Evaluation of CAD patients’ sera potential to induce adherence of human monocytes to cultured endothelial cells (CO).
Task 3.6. Isolation of monocytes from CAD patients’ blood and quantification of their potential to adhere to cultured human endothelial cells (CO)
Task 3.7. Dissemination of the results and research stages; national and international mobility (CO, P1).
MAIN RESULTS OBTAINED DURING PHASE III (01.01-31.12.2014)
The main objective of the third stage (2014) of the PCCA 127 project was to evaluate in vitro the effect of CAD patients’ sera on the production of identified biomarkers by cultured human macrophages, as well as the assessment of patients’ circulating monocytes. The analyzed subjects were divided into: stable angina (SA), unstable angina (UA) and one month after inception of myocardial infarction (MMI) patients, as compared to subjects at risk for CAD without cardiac events (HR) and healthy subjects (C).
After analyzing the data obtained during the third phase of the BIOMARCAD project, the following partial conclusions were drawn:
- the obtained clinical and biochemical data were included in SPSS 21 database for further statistical analysis of all patients after 24 months follow-up,;
- we observed a preferential distribution of miR-486, miR-92a, miR-125a and miR-146a in circulating HDL as compared to LDL, mostly in vulnerable CAD patients;
- SA and UA patient’s sera induced an increased MMP-14 expression in human THP-1 macrophages as illustrated by immunohistochemistry analysis. We observed that sera of MMI patients induced a weaker expression of MMP-14, probably due to their complex anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory treatment (Figure 1);
- the protein expression of IL-33 was lower in human macrophages incubated with CAD patients’ sera compared to control sera as demonstrated by immunohistochemistry analysis; IL-33 expression in cells incubated with sera from MMI patients did not differ from that induced by control sera, probably due to the beneficial effects of their current treatment;
- VAP-1 was not detectable in human macrophages by using the immunohistochemistry technique;
- sera from vulnerable CAD patients increased the expression of miR-486, miR-92a, miR-125a and miR-146a in human macrophages, correlated with the induction of the gene expression of miRNA processing machinery’s components (Dicer, Drosha, DGCR8). The hyperglycemic sera amplified the expression of the mentioned miRNAs (Figure 2).
- the adherence of monocytes isolated from healthy subjects or CAD patients to cultured vascular endothelial cells in the presence of CAD patients’ sera was not significantly different between the patients’ groups.
The new budget cutoff in 2014 affected again the planned activity (first time modified in 2013), some tasks were re-planned for the next stages, hoping that the funds reduced in 2014 will be reallocated in 2015-2016, an absolutely necessary condition for the validation and confirmation of the obtained results and their successful publication in ISI journals.
We noted the existence of a difficulty inunderstanding the obtained data because of the extensive treatment of CAD patients that influencesthe results (statins, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers).
The dissemination of the 2014 results consisted in 4 articles published in ISI-ranked journals (cumulative ISI impact factor: 6.87), 6 communications as invited speaker or with poster at international scientific meetings (2 published as abstract in ISI-ranked journals) and 4 communications at national meetings; we highlight that in all dissemination deliverables we have mentioned the funding from PCCA127 project.
In conclusion, the reported clinical and biochemical data, as well as the number of papers published in ISI-ranked journals and/or communicated at international and national scientific meetings in the Third Phase of BIOMARCAD study confirm the integral fulfilment of the objectives and tasks proposed in the contract PCCA 127 (and the Addendum 2/2014) for the year 2014.

Figure 1. Immune detection of MMP-14 in human macrophages (obtained by PMA-activation of THP-1 monocyte) incubated with CAD sera for 24h. Measurements were done using a monoclonal antibody from Abcam, UK (MMP-14) and a confocal microscope Leica TCS-SP5. (please click to enlarge image)
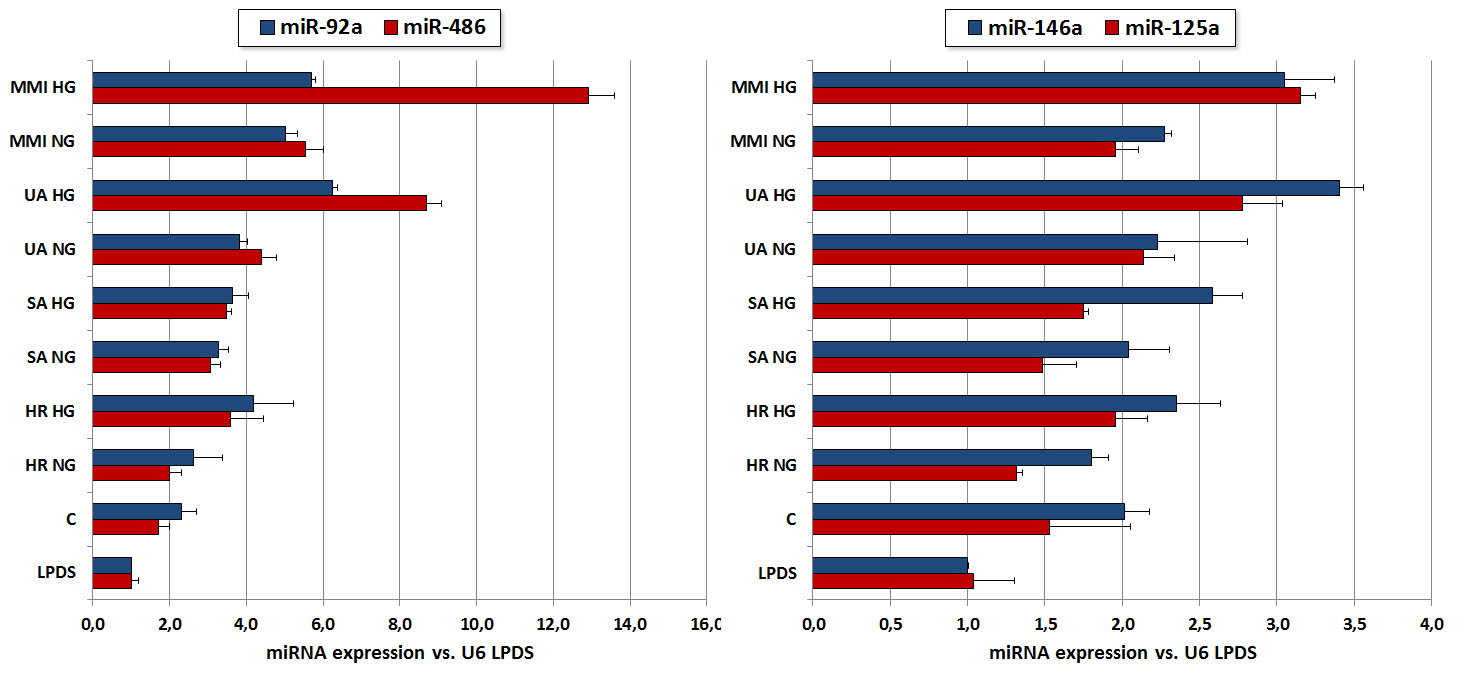
Figure 2. Expression of miR-486, miR-92a, miR-125a and miR-146a in human macrophages incubated with sera from Control subjects (C) and normoglycemic (NG) and hyperglycemic (HG), CAD patients as compared with human delipidated serum (LPDS). Relative average values (2-ΔΔCq) normalized to snRN U6 expression in cells incubated with LPDS. (please click to enlarge image)
DISSEMINATION ACTIVITIES
Scientific articles
Simionescu N., L.S. Niculescu, G.M. Sanda, D. Margina, A.V. Sima. Analysis of circulating microRNAs that are specifically increased in hyperlipidemic and/or hyperglycemic sera. Molec. Biol. Rep. 41(9): 5765-73, 2014 (2013 IF 1.958).
Niculescu L.S., G.M. Sanda, N. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Bilberries exert an anti-atherosclerotic effect in lipid-loaded macrophages. Centr. Eur. J. Biol. 9(3): 268-276, 2014 (2013 IF 0.633).
Stancu C.S., Sanda G.M., Deleanu M., Sima A.V., Probiotics determine hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects, Mol. Nutr. Food Res 58(3):559-68, 2014 (2013 IF 4.909).
Simionescu, N., Niculescu, L.S., Sanda, G.M., Margina, D., Sima, A.V., Serum microRNA profiling of hyperlipidemic and/or hyperglycemic patients reveals specifically increased levels of miR-122, miR-125a, miR-486 and miR-92a, Annals Romanian Society of Cell Biology, XIX(1): 55 – 66, 2014 (BDI, non-ranked ISI journal).
Niculescu L.S., N. Simionescu, G.M. Sanda, M.G. Carnuta, C.S. Stancu, A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, A. Munteanu (Vlad), D.R. Dimulescu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Identification of microRNAs in serum lipoproteins from coronary artery disease patients; miR-486 and miR-92a associate with disease vulnerability. Manuscript in preparation.
International Scientific Meetings
Oral communication
Simionescu N., L.S. Niculescu, G.M. Sanda, D. Margina, A.V. Sima. Identification of micro-RNAs in lipoproteins from hyperlipidemic and/or hyperglycemic sera. The 6th National Congress with International Participation and 32nd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Targu Mures, 4-7 June 2014, Bulletin of RSCB 42, p. 48, 2014.
Carnuta M.G., Stancu C.S., Deleanu M., Sanda G.M., Sima A.V., The study of dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins from patients with coronary artery disease. The 6th National Congress with International Participation and 32nd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Targu Mures, 4-7 June 2014, Bulletin of RSCB 42, p. 47, 2014.
Poster communications
Popescu M.R., C.S. Stancu, M. Deleanu, L.S. Niculescu, N. Simionescu, A. Vlad, A.C. Popescu, D. Dimulescu, A.V. Sima. Novel biomarkers and the activity of the coronary artery disease. Third Frontiers in CardioVascular Biology Meeting (FCVB), Barcelona, Spain, 4-6 iulie 2014, Cardiovasc. Res. 103(Suppl. 1): S44-S45, DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvu082.181, 2014 (IF 5,808).
Niculescu L.S., N. Simionescu, A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, D. Dimulescu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Circulating miRNA and the severity of coronary artery disease. European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 30 august 2014 - 3 septembrie 2014, Eur. Heart J. 35(Suppl. 1): 223, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu323 173-512, 2014 (IF 14,723).
Niculescu L.S., N. Simionescu, G.M. Sanda, A.C. Popescu, R.M. Popescu, D.R. Dimulescu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Analysis of circulating micro-RNAs in lipoprotein fractions isolated from sera of coronary artery disease patients. The 6th National Congress with International Participation and 32nd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Targu Mures, 4-7 June 2014, Bulletin of RSCB 42, p. 109, 2014.
Stancu C.S., G.M. Sanda, M.G. Carnuta, L.S. Niculescu, M. Deleanu, D. Rogoz, A.C. Popescu, R.M. Popescu, D.R. Dimulescu, A.V. Sima. Novel predictive biomarkers associated to lipoproteins - indicators for the evolution of coronary artery disease. The 6th National Congress with International Participation and 32nd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Targu Mures, 4-7 June 2014, Bulletin of RSCB 42, p. 106, 2014.
National Scientific Meetings
Invited speaker
Sima A.V., L.S. Niculescu, G.M. Sanda, C.S. Stancu, L. Toma, M. Deleanu, N. Simionescu, M.G. Carnuta. Ateroscleroza coronariana: biomarkeri asociati lipoproteinelor circulante. Simpozion aniversar IBPC-NS 35 ani de activitate: „De la cercetarea fundamentala si preclinica la medicina personalizata”, Academia Romana, Bucuresti, 10 decembrie 2014.
Sanda G.M., L.S. Niculescu, N. Simionescu, A.V. Sima, M. Simionescu. Macrofage umane in cultura expuse la LDL oxidat secreta CRP si MMP-9; efectul protector al extractului de afine. Simpozion aniversar IBPC-NS 35 ani de activitate: „De la cercetarea fundamentala si preclinica la medicina personalizata”, Academia Romana, Bucuresti, 10 decembrie 2014.
Poster communications
Niculescu L.S., Simionescu N., A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, D.R. Dimulescu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Circulating miRNA and the severity of coronary artery disease. Al 53-lea Congres National de Cardiologie, Sinaia, 2-4 octombrie 2014, Romanian Journal of Cardiology Supplement A, 33-34, 2014.
Deleanu M., G.M. Sanda, C.S. Stancu, A.V. Sima. Determination of fatty acids composition and their peroxidation products in atherogenic low density lipoproteins. A 33a Conferinta Nationala de Chimie cu Participare Internationala, Calimanesti-Caciulata, 1-3 octombrie 2014, Abstract book, Postere - Sectiunea 1, p. 5, 2014.
Title: Setting up of an in vitro experimental model to evaluate the effect of the sera of CAD patients on the production of inflammatory molecules by cultured endothelial cells
Period: 01 January 2015 – 31 December 2015
Objective: To evaluate in vitro the effect of CAD patients’ sera on the production of the identified biomarkers by cultured endothelial cells
Task 4.1. Follow-up of all patients at 36 months (M36); blood collection, clinical and biochemical analysis (P1)
Task 4.2. Quantification of patients’ sera inflammatory potential by measuring the induced secretion of miRNAs, sVAP-1, sIL-33, DPP-4 and MMP-14 by cultured human endothelial cells; immunolocalization of cellular VAP-1, IL-33, DPP-4 and MMP-14 (CO)
Task 4.3. Evaluation of the newly proposed biomarkers (sVAP-1, IL-33, DPP-4, MMP-14) in the adherence of monocytes to cultured human endothelial cells exposed to patients’ sera (CO)
Task 4.4. Dissemination of the results and research stages; national and international mobility (CO, P1)
MAIN RESULTS OBTAINED DURING PHASE IV (01.01-31.12.2015)
- CAD patients’ sera increased the expression of miR-25, miR-92a, miR-125a and miR-146a in human endothelial cells (EAh926), in particular for sera from vulnerable CAD patients, while miR-486 expression was not modified, compared to control sera (Figure 1);
- the increased expression observed for the analyzed miRNAs did not correlate with the expression of miRNA processing machinery components (Dicer, Drosha, DGCR8), other mechanisms being possibly involved;
- UA and MMI patients’ sera have a higher capacity to induce MMP-14 expression in human endothelial cells, compared to control sera;
- protein expression of IL-33 was stronger in human endothelial cells incubated with control sera, compared to SA, UA and MMI sera;
- UA and MMI patients’ sera induced a more pronounced expression for DPP-4 in human endothelial cells, compared to SA patients and control subjects;
- VAP-1 was undetectable in human endothelial cells;
- the adherence of CD14+ monocytes isolated from healthy controls to human endothelial cells in the presence of CAD patients’ sera (SA, UA) was significantly increased compared to control sera and was higher for UA compared to SA sera.

Figure 1. MiRNA expression in human endothelial cells EA.hy926 after 24h incubation with CAD patient’s and healthy control sera.
DISSEMINATION ACTIVITIES
Scientific articles
Stancu C.S., Carnuta M.G., Sanda G.M., Toma L., Deleanu M., Niculescu L.S., Sasson S., Simionescu M., Sima A.V. Hyperlipidemia-induced hepatic and small intestine ER stress and decreased paraoxonase 1 expression and activity is associated with HDL dysfunction in Syrian hamsters. Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 59(11): 2293–2302,2015 (2014 IF 4,603; Q1 category - Web of Science).
Niculescu L.S., Simionescu N., Sanda G.M., Carnuta M.G., Stancu C.S., Popescu A.C., Popescu M.R., Vlad A., Dimulescu D.R., Simionescu M., Sima A.V. MiR-486 and miR-92a identified in circulating HDL discriminate between stable and vulnerable coronary artery disease patients. PLOS One, 10(10): e0140958, 2015 (2014 IF 3,234; Q1 category - Web of Science; awarded 2015 UEFISCDI).
Sanda G.M., Deleanu M., Simionescu M., Sima A.V. Oxidized LDL induce C-reactive protein secretion in human macrophages through mechanisms involving oxidative stress. Annals of R.S.C.B., XIX(3): 9-20, 2015 (BDI, non-ranked ISI journal).
Deleanu M., Sanda G.M., Stancu C.S., Popa M.E., Sima A.V. Profiles of fatty acids and the main lipid peroxidation products of human atherogenic low density lipoproteins, Rev. Chim. 67 (1), 2016.
Oral communications
Sanda G.M., Deleanu M., Sima A.V., Simionescu M. Oxidized LDL induce the expression of pro-inflammatory molecules in lipid-loaded macrophages. The 4th International Symposium on Adipobiology and Adipopharmacology (ISAA), Bucharest, 28-31 October 2015, Rom. J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis., 22(2): 31-32, 2015.
Stancu C.S., Carnuta M.G., Sanda G.M., Toma L., Deleanu M., Sima A.V.. Dysfunctional HDL in the small intestine of hyperlipidemic hamsters is generated by the increased ER stress; reverse effect of lowering intestinal lipid transport by probiotics. The 4th International Symposium on Adipobiology and Adipopharmacology (ISAA), Bucharest, 28-31 October 2015, Rom. J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis., 22(2): 35-36, 2015.
Niculescu L.S., Simionescu N., Sanda G.M., Sima A.V.. Lipoproteins as circulating nanocarriers of microRNAs. The 7th National Congress with International Participation and 33rd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Baia Mare, 11-14 June 2015, Bulletin of RSCB 43, p. 22, 2015.
Sanda G.M., Niculescu L.S., Rogoz D., Sima A.V., Simionescu M.. Molecular mechanisms underlying oxLDL-induced MMP-9 secretion in human macrophages. The 7th National Congress with International Participation and 33rd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Baia Mare, 11-14 June 2015, Bulletin of RSCB 43, p. 54, 2015.
Carnuta M.G., Stancu C.S., Deleanu M., Sanda G.M., Sima A.V.. Paraoxonase 1 protein and activity is decreased in serum and high density lipoproteins from vulnerable coronary artery disease patients. The 7th National Congress with International Participation and 33rd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Baia Mare, 11-14 June 2015, Bulletin of RSCB 43, p. 40, 2015 (Best Oral Presentation Award).
Simionescu N., Niculescu L.S., Sima A.V.. Analysis of microRNAs in high density lipoproteins isolated from the sera of coronary artery disease patients. The 7th National Congress with International Participation and 33rd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Baia Mare, 11-14 June 2015, Bulletin of RSCB 43, p. 41, 2015.
Poster communications
Deleanu M., Sanda G.M., Sima A.V.. Determination of 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α in human plasma by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. The 18th International Conference „Physical Methods in Coordination and Supramolecular Chemistry”, Chisinau, Moldova, 8-9 October 2015, Book of Abstracts, p. 61, 2015 (Best Poster Presentation Award).
Stancu C.S., Sanda G.M., Deleanu M., Carnuta M.G., Toma L., Niculescu L.S., Sima A.V.. Molecular mechanisms linking hyperlipidemia with dysfunctional HDL; decreased expression of paraoxonase 1 in the small intestine, liver and serum of hyperlipidemic hamsters and the association with aortic valves lesions. The 38th European Lipoprotein Club Scientific Meeting, Tutzing, Germany, 7-10 September 2015, Book of Abstracts, p. 71, 2015.
Niculescu L.S., Simionescu N., Sanda G.M., Sima A.V.. MiR-486 and miR-92a identified in circulating HDL discriminate between stable and vulnerable coronary artery disease patients. The 38th European Lipoprotein Club Scientific Meeting, Tutzing, Germany, 7-10 September 2015, Book of Abstracts, p. 87, 2015.
Simionescu N., Niculescu L.S., Sanda G.M., Popescu A.C., Popescu M.R., Munteanu A., Dimulescu D.R., Sima A.V.. MiR-486 and miR-92a identified in HDL subfractions discriminate between stable and vulnerable coronary artery disease patients. The 15th Annual FEBS Young Scientists' Forum (YSF) and the 40th Congress of The Federation of European Biochemical Societies (FEBS), Berlin, Germany, 2-9 July2015, FEBS J. 282(S1): 217, 2015 (IF 4,001).
Toma L., Sanda G.M., Deleanu M., Rogoz D., Sima A.V.. Caffeic acid ameliorates endothelial dysfunction induced by glycated LDL. The 7th National Congress with International Participation and 33rd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Baia Mare, 11-14 June 2015, Bulletin of RSCB 43, p. 62, 2015.
Stancu C.S., Sanda G.M., Carnuta M.G., Deleanu M., Toma L., Niculescu L.S., Rogoz D., Sima A.V.. Molecular mechanisms linking hyperlipidemia with dysfunctional HDL; decreased expression of paraoxonase 1 in the small intestine, liver and serum of hyperlipidemic hamsters and the association with aortic valves lesions. The 7th National Congress with International Participation and 33rd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Baia Mare, 11-14 June 2015, Bulletin of RSCB 43, p. 91, 2015.
Deleanu M., Sanda G.M., Toma L., Popa M.E., Sima A.V.. The effect of modified low density lipoproteins on the oxidative stress and lipid loading of human endothelial cells and macrophages. The 7th National Congress with International Participation and 33rd Annual Scientific Session of Romanian Society for Cell Biology, Baia Mare, 11-14 June 2015, Bulletin of RSCB 43, p. 129, 2015.
Research stages
Ph.D. students Natalia Simionescu and Mihaela Carnuta attended the International Atherosclerosis Research School (iARS), organized by European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), in Prague, Czech Republic, between 23-29 August 2015.
PHASE V
Title: Assessment of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) and markers of circulating monocytes in CAD patients’ blood; validation of the predictive potential of the identified biomarkers for the CAD evolution.
Objective 1: Assessment of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) and markers on circulating monocytes in CAD patients’ blood.
Task 5.1. Follow-up of all patients at 48 months; blood collection and biochemical analysis (P1).
Task 5.2. Quantification of circulating EPC number from the blood of CAD patients (CO).
Task 5.3. Quantification of markers expressed on the CAD patients monocytes surface (TLR4, CD11b, CD16) (CO);
Task 5.4. Evaluation of the new proposed biomarkers (sVAP-1, DPP4, IL-33, MMP-14) and the makers expressed on circulating monocytes (TLR4, CD11b, CD16) from patients’ blood (CO).
Objective 2: Validation of the predictive potential of the identified biomarkers for the CAD evolution; to establish the transfer of methodology for detection of the new biomarkers in the clinic laboratory.
Task 5.5. Statistical analysis of the correlation between the proposed biomarkers and major coronary events during the 4 years follow-up (CO, P1).
Task 5.6. Transfer of methodology for evaluation of newly proposed and validated biomarkers from bench to clinic. (CO, P1)
Task 5.7. Final meeting of the consortium to elaborate the prognosis protocol that should discriminate between the progression of CAD in patients by using the newly proposed biomarkers. (CO, P1)
MAIN RESULTS OBTAINED DURING PHASE V (01.01-31.12.2016)
- Recruitment of 19 new patients, up to a total of 153 CAD patients with stable angina (SA) or with acute coronary syndrome (ACS, unstable angina and patients at one-month follow-up after AMI) and 30 healthy Control subjects;
- Finished the building of a biobank with sera, plasma and urine samples, plasma RNAs and circulating blood cells (PMBC, CD14+ monocytes), kept in liquid nitrogen or deep-freezers at -86°C;
- The populations of CD45dim/CD34+/CD309+ EPC and of CD14+ monocytes in SA and ACS patients proved lower than in Control subjects (Figure 1);
- The number of non-classical pro-inflammatory CD14++CD16+ monocytes was decreased in SA and ACS patients compared to Control subjects;
- The subpopulation of CD14+/CD11b+ monocytes (involved in trans-endothelial migration) was lower in SA compared with ACS patients and Control subjects;
- The activation level of circulating monocytes, expressed by TLR4 receptor, was lower in subsets of monocytes isolated from SA and ACS patients compared with Control subjects;
- The correlations between the proposed parameters that define the inflammatory status and the monocytes subsets are modest and without statistical significance;
- By using a statistical model of binary logistic regression, the most important contribution to the prediction of coronary events risk are three circulating miRNAs (miR-92a, miR-486 and miR-122) and the activity of serum paraoxonase 1 (PON1).
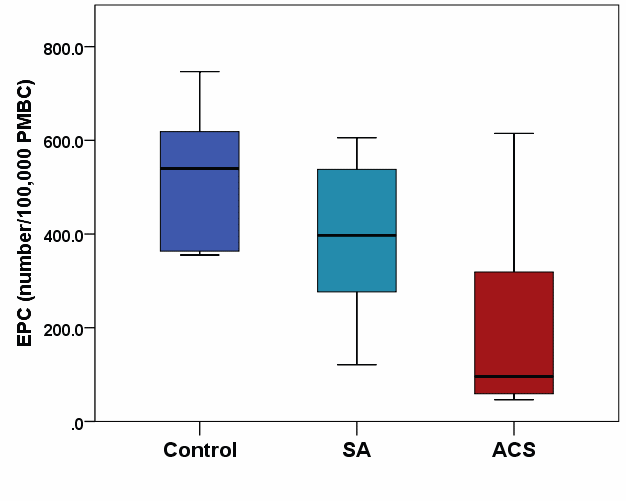
Figure 1. Box-plot distribution of endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) in the blood from CAD patients and control subjects,
analyzed using CD45dim/CD34+/CD309+ markers by flow cytometry (Gallios, Beckman-Coulter).
DISSEMINATION ACTIVITIES
Scientific articles
Simionescu N., L. S. Niculescu, G.M. Sanda, M.G. Cărnuţă, C.S. Stancu, A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, A. Vlad, D.R. Dimulescu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Hyperglycemia Determines Increased Specific MicroRNAs Levels in Sera and HDL of Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients and Stimulates MicroRNAs Production in Human Macrophages. PLoS ONE 11(8): e0161201, 2016. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161201; [2015 IF 3,54]; awarded 2016 UEFSCDI.
Toma L., G.M. Sanda, M. Deleanu, C.S. Stancu, A.V. Sima. Glycated LDL Increase VCAM-1 Expression and Secretion in Endothelial Cells and Promote Monocyte Adhesion through Mechanisms Involving Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 417(1-2):169-79, 2016.doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2724-z; [2015 IF 2,613]
Sanda G.M., M. Deleanu, L. Toma, C.S. Stancu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Oxidized LDL-Exposed Human Macrophages Display Increased MMP-9 Expression and Secretion Mediated by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016 Jun 24; doi: 10.1002/jcb.25637. accepted-in press. [2015 IF 3,49].
Deleanu M., G. M. Sanda, C. S. Stancu, M.E. Popa, A.V. Sima. Profiles of Fatty Acids and the Main lipid Peroxidation Products of Human Atherogenic Low Density Lipoproteins. Revista de Chimie 67(1): 8-12, 2016. [2015 IF 0,956]
Oral communications
Sima A.V. Correlation between microRNAs and coronary artery disease’s severity. Invited Lecture at Romanian Society of Hypertension Congress ”Arterial Hypertension - interferences and connections”, Bucharest, 15-17 September 2016.
Stancu C.S., M. G. Cărnuță, G. M. Sanda, A. C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, A. Vlad, D. R. Dimulescu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Paraoxonase 1, Oxidation Products and ApoA-II Levels in HDL3 Discriminate between Acute Coronary Syndrome and Stable CAD Patients. Oral Communication at 55th National Congress of the Romanian Society of Cardiology, Sinaia, 21-24 September 2016, Romanian Journal of Cardiology Supplement2016.
Poster communications
Stancu C.S., M.G. Cărnuţă, G.M. Sanda, L. Toma, M. Deleanu, L.S. Niculescu, A.V. Sima. Fat-activated ER stress induces the reduction of ABCG5/8 expression in the small intestine and liver of hyperlipidemic hamsters and the appearance of dysfunctional HDL. 84th Congress of European Atherosclerosis Society, Innsbruck, Austria, 29 May - 2 June 2016, AtherosclerosisSupplem. 252: e108, September 2016, DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.07.596.
Toma L., G.M. Sanda, M. Deleanu, C.S. Stancu, A.V. Sima. Glycated LDL Induce Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Along with the Stimulation of VCAM-1 Expression in Human Endothelial Cells, and The Ensuing Monocyte Adhesion. 84th Congress of European Atherosclerosis Society, Innsbruck, Austria, 29 May - 2 June 2016, AtherosclerosisSupplem. 252: e158-e159, September 2016, DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.07.765.
Sanda G.M., M. Deleanu, C.S. Stancu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Human macrophages exposed to oxidized LDL or tunicamycin exhibit increased MMP-9 expression, secretion and activity by a mechanism involving ER stress. 84th Congress of European Atherosclerosis Society, Innsbruck, Austria, 29 May - 2 June 2016, AtherosclerosisSupplem. 252: e171, September 2016, DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.07.808.
Niculescu L.S., N. Simionescu, G.M. Sanda, M.G. Cărnuţă, C.S. Stancu, A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, A. Vlad, D.R. Dimulescu, A.V. Sima. Hyperglycemia increases microRNAs in circulating HDL from acute coronary syndrome patients and modulates miRNA processing machinery in human macrophages. 84th Congress of European Atherosclerosis Society, Innsbruck, Austria, 29 May - 2 June 2016, Atherosclerosis Supplem. 252:e82, September 2016. DOI: 10.1016/ j.atherosclerosis.2016.07.504.
Niculescu L.S., N. Simionescu, G.M. Sanda, M.G. Cărnuţă, C.S. Stancu, A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, A. Vlad, D.R. Dimulescu, A.V. Sima. Specific circulating microRNAs levels associate with hypertension, hyperglycemia and dysfunctional HDL in acute coronary syndrome patients. Poster presentation at 4th Frontiers in Cardiovascular Biology, Florence, Italy, 8–10 July 2016, Cardiovascular Research, 111(Suppl 1): S56-S81, 2016; DOI: http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/cvr/cvw149.
Niculescu L.S., N. Simionescu, G.M. Sanda, A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, A. Vlad, D.R. Dimulescu, M. Simionescu, A.V. Sima. Hyperglycemia is Associated with Increased Circulating Micrornas Levels in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients’ Sera and Determines the Upregulation of microRNA Production in Human Macrophages. Moderated poster at 55th National Congress of the Romanian Society of Cardiology, Sinaia, 21-24 September 2016, Romanian Journal of Cardiology Supplement2016. Poster awarded by the Program of Romanian cardiology Society - Awarding the Excellence in Research.
Niculescu L.S., N. Simionescu, G.M. Sanda, M.G. Cărnuţă, C.S. Stancu, A.C. Popescu, M.R. Popescu, A. Vlad, D.R. Dimulescu, A.V. Sima. Hyperglycemia Increases Micro-RNAs in Sera and HDL From Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients; in Search for the Processing Machinery of Micro-RNAs in Human Macrophages. Poster presentation at 8th National Congress with international participation and 34th Annual scientific session of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 8-12 June 2016, Oradea, Bulletin of RSCB 44: 63, 2016.
Cărnuţă M.G., C.S. Stancu, G.M. Sanda, L. Toma, M. Deleanu, L.S. Niculescu, Anca V. Sima. Fat-Activated ER Stress Induces the Reduction of ABCG5/8 Expression in the Small Intestine and Liver of Hyperlipidemic Hamsters and the Appearance of Dysfunctional HDL. Poster presentation at 8th National Congress with international participation and 34th Annual scientific session of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 8-12 June 2016, Oradea, Bulletin of RSCB 44: 62, 2016.
Deleanu M., C. S. Stancu, M. E. Popa, A.V. Sima. Preparation and Characterization of Nanoemulsion Encapsulating Ginger Extract. A XXXlV-a Conferinţă Naţională de Chimie, Călimănești-Căciulata, 4-8 Octomber 2016.
Stancu C.S., M. G. Cărnuţă, G. M. Sanda, L. Toma, M. Deleanu, L. S. Niculescu, A. V. Sima. The Hyperlipidemic Diet Inhibits ABC Transporters in the Intestine and Liver of Hamsters and Induces HDL Dysfunction. Al V-lea Simpozion Naţional ARSAL cu participare internaţională, Bucureşti, 10 - 11 noiembrie 2016.

